Home>Health & Nutrition>Injury Prevention>Overcoming Plantar Pain In Just Four Weeks

Injury Prevention
Overcoming Plantar Pain In Just Four Weeks
Published: March 1, 2024
Learn effective injury prevention strategies to overcome plantar pain in just four weeks. Discover expert tips and exercises to keep your feet healthy and pain-free.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
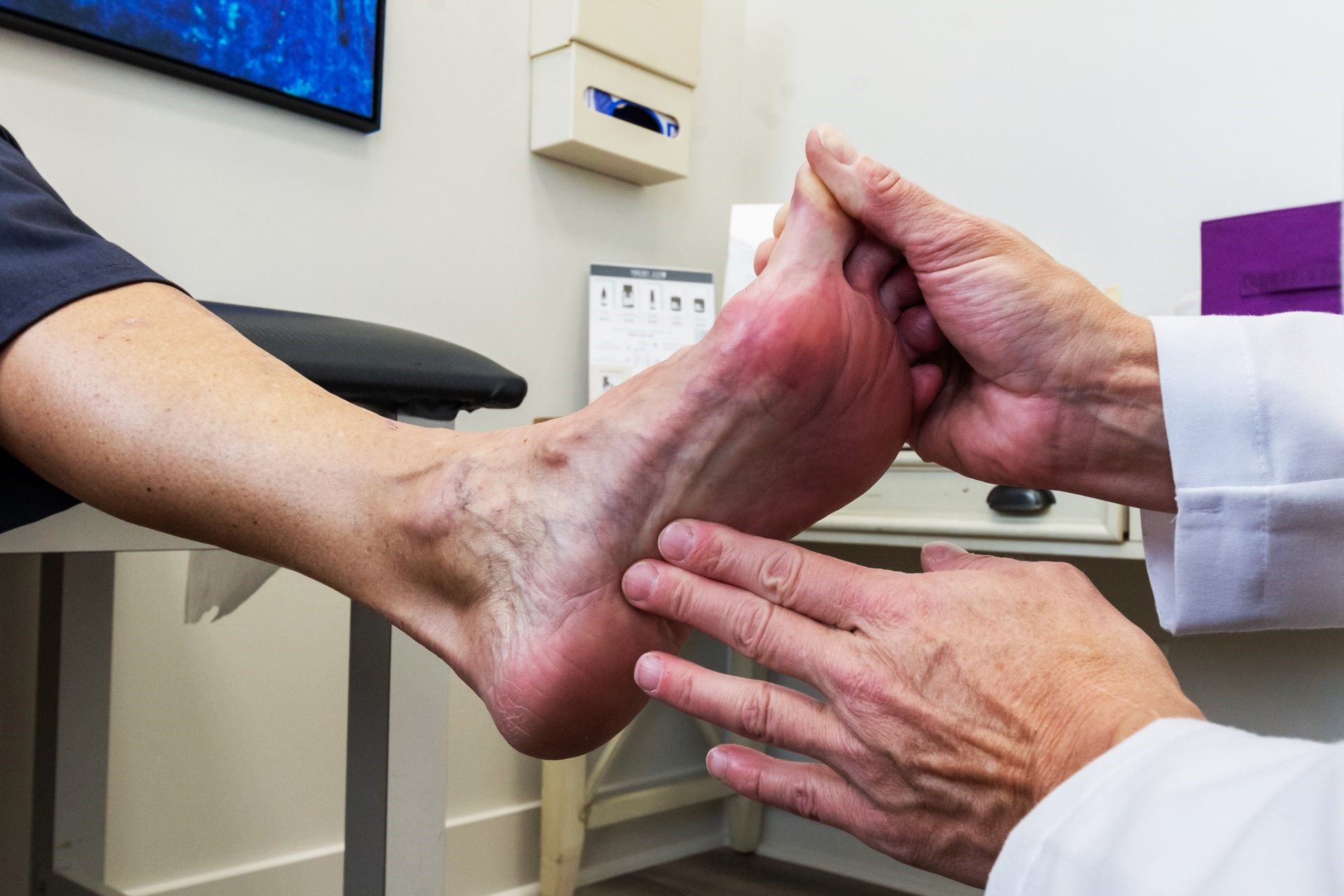
Understanding Plantar Pain
Plantar pain, also known as plantar fasciitis, is a common foot condition characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs across the bottom of the foot, connecting the heel bone to the toes. This condition often leads to stabbing pain near the heel, especially with the first few steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest.
The plantar fascia plays a crucial role in supporting the arch of the foot and absorbing the impact of walking, running, and other weight-bearing activities. When this tissue is strained or overused, small tears can develop, leading to inflammation and pain. Plantar pain is often associated with activities that put stress on the heel and arch, such as running, dancing, or standing for extended periods.
Understanding the underlying causes of plantar pain is essential for effective treatment and prevention. Factors such as overpronation (excessive inward rolling of the foot), high arches, flat feet, improper footwear, obesity, and repetitive strain from certain activities can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis.
In addition to physical factors, lifestyle habits and occupational demands can also play a role in the onset of plantar pain. Individuals who engage in activities that place repetitive stress on the feet, such as long-distance running or standing for prolonged periods, are at a higher risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
Moreover, age and inadequate foot support can exacerbate the condition, as the plantar fascia loses elasticity over time and may become more susceptible to injury. Understanding the multifaceted nature of plantar pain empowers individuals to take proactive measures to address the root causes and alleviate discomfort.
By gaining insight into the intricate interplay of biomechanical, lifestyle, and environmental factors contributing to plantar pain, individuals can make informed decisions about treatment and prevention strategies. This comprehensive understanding serves as a foundation for developing a holistic approach to managing plantar fasciitis and promoting long-term foot health.
Causes of Plantar Pain
Plantar pain, or plantar fasciitis, can stem from a variety of factors, each contributing to the strain and inflammation of the plantar fascia. Understanding these causes is crucial in addressing the condition effectively and preventing its recurrence.
-
Biomechanical Factors: Irregularities in foot structure and mechanics can significantly impact the distribution of weight and pressure on the feet. Overpronation, where the foot rolls inward excessively, or high arches can lead to increased tension on the plantar fascia, making it more susceptible to injury. Similarly, individuals with flat feet may experience altered foot mechanics, placing additional stress on the plantar fascia.
-
Improper Footwear: Wearing unsupportive or ill-fitting shoes can exacerbate plantar pain. Shoes with inadequate arch support, insufficient cushioning, or poor shock absorption fail to provide the necessary protection for the plantar fascia during weight-bearing activities. High heels and shoes with inadequate toe space can also contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis.
-
Repetitive Strain: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive impact on the feet, such as running, dancing, or standing for prolonged periods, can strain the plantar fascia. The cumulative effect of these activities can lead to microtears in the tissue, triggering inflammation and pain.
-
Obesity: Excess body weight places increased pressure on the feet, particularly the plantar fascia. The additional load can overstress the tissue, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Managing body weight is essential in reducing the strain on the feet and mitigating the risk of plantar fasciitis.
-
Age-Related Changes: As individuals age, the plantar fascia may lose some of its elasticity and resilience. This natural aging process can make the tissue more vulnerable to injury and inflammation, increasing the likelihood of developing plantar pain.
-
Occupational Factors: Certain occupations that involve prolonged standing or walking on hard surfaces can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis. Workers in professions such as teaching, healthcare, and retail, which require long hours on their feet, are at a higher risk of experiencing plantar pain due to the repetitive stress placed on the plantar fascia.
By recognizing these diverse causes of plantar pain, individuals can take proactive measures to address the underlying factors contributing to the condition. Implementing targeted interventions, such as corrective footwear, biomechanical adjustments, weight management, and ergonomic considerations in the workplace, can help alleviate plantar pain and promote long-term foot health.
Treatment Options for Plantar Pain
Addressing plantar pain requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses various treatment modalities aimed at reducing inflammation, alleviating discomfort, and promoting the healing of the plantar fascia. By combining conservative measures with targeted interventions, individuals can effectively manage plantar fasciitis and facilitate a gradual return to pain-free mobility.
1. Rest and Ice
Resting the affected foot is paramount in allowing the inflamed plantar fascia to heal. Minimizing weight-bearing activities and providing adequate rest to the foot can prevent further aggravation of the condition. Additionally, applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Cold therapy, in the form of ice packs or frozen water bottles, can be applied for 15-20 minutes several times a day to provide relief.
2. Supportive Footwear
Wearing supportive footwear with proper arch support and cushioning is essential for individuals with plantar pain. Shoes that provide adequate shock absorption and stability can help reduce the strain on the plantar fascia during daily activities. Additionally, orthotic inserts or custom-made shoe inserts can offer targeted support and alignment, promoting optimal foot mechanics and reducing discomfort.
3. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Engaging in specific stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve the flexibility and strength of the muscles and ligaments surrounding the foot and ankle. Calf stretches, toe curls, and towel scrunches are examples of exercises that can aid in relieving tension in the plantar fascia and promoting overall foot function. These exercises should be performed regularly to enhance the resilience of the foot structures and reduce the risk of recurrent plantar pain.
4. Physical Therapy
Seeking guidance from a physical therapist can provide valuable insights into targeted exercises and techniques to address plantar fasciitis. Physical therapy sessions may include manual therapy, ultrasound, and specialized exercises tailored to the individual's specific needs. The expertise of a physical therapist can contribute to a comprehensive rehabilitation plan and facilitate a gradual return to normal activities.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with plantar fasciitis. These medications can provide short-term relief from discomfort and help manage the inflammatory response within the affected tissue. However, it is important to use these medications as directed and consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
6. Night Splints
Night splints are designed to maintain a gentle stretch in the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon while the individual sleeps. By preventing the tightening of these structures during rest, night splints can help reduce morning pain and stiffness commonly experienced by individuals with plantar fasciitis. Incorporating night splints into the treatment regimen can contribute to improved mobility and reduced discomfort upon waking.
7. Corticosteroid Injections
In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be considered to alleviate severe pain and inflammation associated with plantar fasciitis. These injections are administered directly into the affected area to provide targeted relief. However, it is important to note that the use of corticosteroid injections is typically reserved for cases that do not respond to conservative treatments and may carry potential risks and limitations.
8. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT)
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy is a non-invasive treatment modality that utilizes shock waves to stimulate the healing process in the affected tissue. ESWT has been shown to promote tissue regeneration and reduce pain in individuals with chronic plantar fasciitis. This innovative approach may offer a viable option for individuals seeking alternative treatments for persistent plantar pain.
By integrating these diverse treatment options, individuals can tailor their approach to managing plantar pain based on their unique needs and preferences. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific underlying factors contributing to plantar fasciitis and promotes effective pain management and recovery.
Four-Week Plan for Overcoming Plantar Pain
Embarking on a structured four-week plan can significantly contribute to the alleviation of plantar pain and facilitate a gradual return to pain-free mobility. This comprehensive plan integrates targeted interventions and progressive strategies to address the underlying causes of plantar fasciitis and promote the healing of the affected tissue.
Week 1: Rest and Assessment
The first week of the plan focuses on providing ample rest to the affected foot to minimize further strain on the inflamed plantar fascia. Individuals are encouraged to avoid high-impact activities and prolonged standing, allowing the tissue to initiate the healing process. During this period, it is essential to assess the severity of the plantar pain and identify any contributing factors, such as footwear choices and biomechanical irregularities.
Week 2: Footwear Evaluation and Modification
In the second week, attention shifts to evaluating the footwear worn on a daily basis. Individuals are advised to assess the support, cushioning, and overall fit of their shoes, ensuring that they provide adequate protection and stability for the feet. If necessary, modifications such as the incorporation of orthotic inserts or the transition to supportive footwear are implemented to optimize foot mechanics and reduce the strain on the plantar fascia.
Week 3: Introduction of Stretching and Strengthening Regimen
As the third week commences, a structured regimen of stretching and strengthening exercises is introduced to enhance the flexibility and resilience of the foot structures. Calf stretches, toe curls, and plantar fascia-specific exercises are incorporated into the daily routine to alleviate tension and promote optimal foot function. Consistent engagement in these exercises contributes to the gradual improvement of foot mechanics and the reduction of discomfort associated with plantar fasciitis.
Week 4: Progressive Activity and Long-Term Strategies
In the final week of the plan, individuals begin to gradually reintroduce low-impact activities, such as walking and light stretching, to gauge the response of the plantar fascia. This progressive approach allows for the gradual resumption of normal activities while monitoring the tolerance of the affected foot. Additionally, long-term strategies for preventing the recurrence of plantar pain, including ongoing stretching routines, footwear considerations, and lifestyle modifications, are emphasized to promote sustained foot health.
By adhering to this structured four-week plan, individuals can proactively address plantar pain and lay the foundation for long-term foot health. The gradual integration of targeted interventions, combined with a focus on prevention and maintenance, empowers individuals to overcome plantar fasciitis and embrace a lifestyle characterized by pain-free mobility and optimal foot function.
Exercises and Stretches for Plantar Pain Relief
Engaging in specific exercises and stretches tailored to alleviate plantar pain can play a pivotal role in promoting the flexibility, strength, and resilience of the foot structures. These targeted interventions aim to reduce tension in the plantar fascia, enhance foot mechanics, and contribute to the overall management of plantar fasciitis.
Calf Stretches
Calf stretches are instrumental in addressing the tightness and inflexibility that can contribute to plantar pain. Performing calf stretches involves standing facing a wall with one foot positioned forward and the other extended behind. By leaning forward while keeping the back heel grounded, individuals can experience a gentle stretch in the calf muscles, which indirectly influences the tension in the plantar fascia. This stretch should be held for 30 seconds and repeated multiple times throughout the day to promote optimal flexibility in the lower leg and foot.
Toe Curls
Toe curls are simple yet effective exercises that target the intrinsic muscles of the foot, promoting strength and dexterity. To perform toe curls, individuals can place a small towel on the floor and use their toes to scrunch and gather the towel toward them. This action engages the muscles in the arch of the foot and the toes, contributing to improved support and stability. Regular practice of toe curls can aid in reducing tension in the plantar fascia and enhancing the overall function of the foot.
Plantar Fascia Stretch
The plantar fascia stretch specifically targets the thick band of tissue running along the bottom of the foot, aiming to alleviate tightness and discomfort. To perform this stretch, individuals can sit with one leg extended and gently pull the toes back toward the shin, feeling a stretch along the underside of the foot. This stretch should be held for 15-30 seconds and repeated several times to promote flexibility and relieve tension in the plantar fascia.
Ankle Flexion and Extension
Ankle flexion and extension exercises contribute to the mobility and resilience of the ankle joint, which in turn influences the mechanics of the foot. Individuals can perform ankle flexion by sitting with the affected foot raised and gently moving the foot up and down, engaging the muscles and ligaments surrounding the ankle. This motion aids in promoting optimal range of motion and reducing stiffness, contributing to the overall relief of plantar pain.
Marble Pickup
Marble pickup exercises provide a dynamic way to strengthen the muscles in the arch of the foot and enhance dexterity. By placing marbles on the floor and using the toes to pick them up and transfer them to a container, individuals engage the muscles in the foot, promoting improved coordination and strength. Regular practice of marble pickup exercises can contribute to the alleviation of plantar pain and the enhancement of foot function.
By incorporating these exercises and stretches into a daily routine, individuals can actively participate in the management of plantar pain and contribute to the overall improvement of foot health. Consistent engagement in these targeted interventions, coupled with a comprehensive approach to addressing the underlying causes of plantar fasciitis, can pave the way for sustained relief and enhanced mobility.
Tips for Preventing Plantar Pain Recurrence
Preventing the recurrence of plantar pain is essential for maintaining long-term foot health and minimizing the risk of persistent discomfort. By implementing proactive measures and adopting healthy habits, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of plantar fasciitis reoccurring. Here are valuable tips for preventing the recurrence of plantar pain:
-
Footwear Considerations: Choosing supportive footwear with adequate arch support, cushioning, and shock absorption is crucial in preventing the recurrence of plantar pain. Individuals should opt for shoes that provide stability and protection for the feet, especially during weight-bearing activities. Additionally, replacing worn-out shoes and incorporating orthotic inserts can further enhance foot support and reduce the risk of strain on the plantar fascia.
-
Gradual Activity Progression: When returning to physical activities or exercise routines after experiencing plantar pain, it is important to progress gradually. Sudden increases in intensity or duration of activities can place undue stress on the feet, potentially leading to a recurrence of plantar fasciitis. By gradually increasing activity levels and allowing the feet to adapt to the demands placed on them, individuals can mitigate the risk of re-injury.
-
Regular Stretching and Strengthening: Maintaining a consistent regimen of stretching and strengthening exercises for the feet, ankles, and lower legs is instrumental in preventing the recurrence of plantar pain. These exercises promote flexibility, resilience, and optimal foot mechanics, reducing the likelihood of excessive strain on the plantar fascia. Incorporating calf stretches, toe curls, and plantar fascia-specific exercises into a daily routine can contribute to sustained foot health.
-
Weight Management: Managing body weight within a healthy range is essential for reducing the strain on the feet and minimizing the risk of plantar pain recurrence. Excess body weight places increased pressure on the plantar fascia, potentially exacerbating the condition. By adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can support overall foot health and reduce the burden on the feet.
-
Ergonomic Considerations: Individuals with occupations that involve prolonged standing or walking should prioritize ergonomic considerations to minimize the risk of plantar pain recurrence. Utilizing supportive footwear, taking regular breaks to rest the feet, and incorporating anti-fatigue mats or insoles in work environments can help alleviate the strain on the plantar fascia and promote sustained comfort during extended periods of standing or walking.
-
Routine Foot Care: Practicing routine foot care, including inspecting the feet for any signs of irritation or discomfort, can aid in early detection of potential issues. Addressing any emerging concerns promptly, such as blisters, calluses, or discomfort, can prevent the exacerbation of foot-related conditions, including plantar fasciitis.
By integrating these preventive measures into daily routines and lifestyle habits, individuals can actively reduce the risk of plantar pain recurrence and foster sustained foot health. Consistency in implementing these tips, coupled with ongoing vigilance and proactive foot care, can contribute to a reduced likelihood of experiencing the discomfort associated with plantar fasciitis in the future.

