Home>Health & Nutrition>Injury Prevention>Understanding And Managing Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: A Comprehensive Guide For Runners

Injury Prevention
Understanding And Managing Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: A Comprehensive Guide For Runners
Published: February 24, 2024
Learn how to prevent patellofemoral pain syndrome and manage it effectively with this comprehensive guide for runners. Discover essential tips and exercises for injury prevention and optimal performance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS), commonly known as runner's knee, is a prevalent and often challenging condition that affects many individuals who engage in running and other high-impact activities. This syndrome manifests as pain around the patella (kneecap) and the surrounding area, leading to discomfort and limitations in physical performance. For runners, PFPS can be particularly frustrating, as it may hinder their training and participation in races.
Understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for PFPS is crucial for runners and fitness enthusiasts. By gaining insight into this condition, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent and address PFPS, thereby minimizing its impact on their running endeavors.
In the following sections, we will delve into the intricacies of PFPS, exploring its origins, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures. By shedding light on these aspects, runners can equip themselves with the knowledge needed to navigate the challenges posed by PFPS and continue pursuing their passion for running with confidence and resilience.
What is Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome?
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) is a prevalent knee condition characterized by pain and discomfort around the patella (kneecap) and the surrounding area. It is a common ailment among runners and individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive knee movements, such as jumping, squatting, and climbing stairs. PFPS is often referred to as "runner's knee" due to its high incidence among runners, particularly those who partake in long-distance running or intense training regimens.
The patella plays a crucial role in facilitating smooth knee movement by acting as a fulcrum for the quadriceps muscles. However, in individuals with PFPS, the patella may fail to track properly within the femoral groove, leading to abnormal stress on the knee joint. This misalignment can result from various factors, including muscle imbalances, overuse, biomechanical issues, and structural irregularities in the knee joint.
The hallmark symptom of PFPS is anterior knee pain, which is often exacerbated during activities that involve knee flexion, such as running, squatting, or sitting for prolonged periods. Individuals with PFPS may also experience a sensation of grinding or popping in the knee joint, along with swelling and stiffness. The pain associated with PFPS can be debilitating, impacting an individual's ability to engage in physical activities and compromising their overall quality of life.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of PFPS is essential for runners, as it enables them to recognize the early signs of this condition and take proactive measures to address it. By gaining insight into the underlying mechanisms of PFPS, runners can make informed decisions regarding their training routines, footwear selection, and injury prevention strategies.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures for PFPS, providing runners with a comprehensive understanding of this condition and empowering them to manage it effectively.
Causes of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome in Runners
The development of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) in runners can be attributed to a myriad of factors, encompassing biomechanical, anatomical, and training-related elements. Understanding these underlying causes is pivotal in devising effective preventive strategies and targeted interventions to mitigate the risk of PFPS.
-
Muscle Imbalances: Runners are susceptible to PFPS due to imbalances in the muscles surrounding the knee joint. Weakness or tightness in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip abductor muscles can disrupt the optimal alignment of the patella, leading to increased stress on the knee during running activities.
-
Faulty Biomechanics: Anomalies in running gait and lower limb alignment can predispose runners to PFPS. Excessive pronation or supination of the foot, inadequate hip stability, and abnormal tracking of the patella within the femoral groove can contribute to the development of PFPS.
-
Overuse and Training Errors: Engaging in high-intensity or prolonged running without adequate rest and recovery can strain the knee joint, resulting in PFPS. Sudden increases in training volume or intensity, inadequate warm-up routines, and running on uneven or hard surfaces can exacerbate the risk of PFPS among runners.
-
Footwear and Running Surface: Ill-fitting or worn-out running shoes can compromise foot and knee alignment, increasing the likelihood of PFPS. Additionally, running on hard or uneven surfaces without proper shock absorption can subject the knee joint to excessive stress, predisposing runners to PFPS.
-
Anatomical Factors: Structural irregularities in the knee joint, such as patellar malalignment, trochlear dysplasia, or abnormal patellar tilt, can contribute to the onset of PFPS in runners. These anatomical variations can disrupt the smooth movement of the patella, leading to anterior knee pain and discomfort during running activities.
By recognizing these multifaceted causes of PFPS in runners, individuals can proactively address modifiable risk factors through targeted strength training, gait analysis, footwear selection, and training modifications. Implementing comprehensive injury prevention strategies tailored to the specific needs of runners can significantly reduce the incidence of PFPS and foster long-term musculoskeletal health and performance.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying the symptoms of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) is pivotal in facilitating timely diagnosis and targeted intervention for runners grappling with this condition. The manifestation of PFPS encompasses a spectrum of discomfort and functional limitations, warranting a comprehensive understanding of its clinical presentation and diagnostic modalities.
Symptoms of PFPS
The hallmark symptom of PFPS is anterior knee pain, typically localized around or behind the patella. This pain is often exacerbated during activities that involve knee flexion, such as running, squatting, or ascending/descending stairs. Runners with PFPS may experience a dull, aching sensation in the front of the knee, accompanied by a feeling of tightness or discomfort upon prolonged sitting with the knees bent. The pain may intensify during or after running sessions, impacting the individual's performance and overall running experience. Additionally, some individuals may report a sensation of grinding or popping in the knee joint, indicative of patellar maltracking and joint irritation. Swelling and stiffness around the knee joint can also accompany PFPS, further impeding the individual's mobility and athletic pursuits.
Diagnosis of PFPS
Diagnosing PFPS involves a comprehensive assessment of the individual's medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, imaging studies to elucidate the underlying pathology. During the physical examination, healthcare providers may evaluate the individual's gait, lower limb alignment, and patellar tracking to identify any biomechanical anomalies contributing to PFPS. Palpation of the patella and surrounding structures can elicit tenderness and localized pain, aiding in the clinical diagnosis of PFPS. Furthermore, specialized maneuvers, such as the patellar grind test and patellar tilt assessment, may be employed to assess patellar maltracking and joint pathology.
In certain instances, imaging studies, such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans, may be utilized to visualize structural irregularities in the knee joint and assess the extent of soft tissue involvement. These imaging modalities can provide valuable insights into patellar alignment, cartilage integrity, and bony morphology, aiding in the accurate diagnosis and formulation of targeted treatment plans for PFPS.
By recognizing the nuanced symptoms and employing a comprehensive diagnostic approach, healthcare providers can effectively discern PFPS from other knee pathologies and tailor personalized management strategies to address the unique needs of runners grappling with this condition. This proactive approach to symptom recognition and diagnostic precision is instrumental in mitigating the impact of PFPS on runners' training regimens and fostering long-term musculoskeletal health and resilience.
Treatment Options for Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Addressing Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) necessitates a multifaceted approach encompassing targeted interventions, rehabilitative measures, and lifestyle modifications tailored to the unique needs of runners grappling with this condition. By integrating evidence-based treatment modalities, healthcare providers can empower individuals with PFPS to regain optimal knee function, alleviate pain, and resume their running pursuits with confidence and resilience.
Conservative Management
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
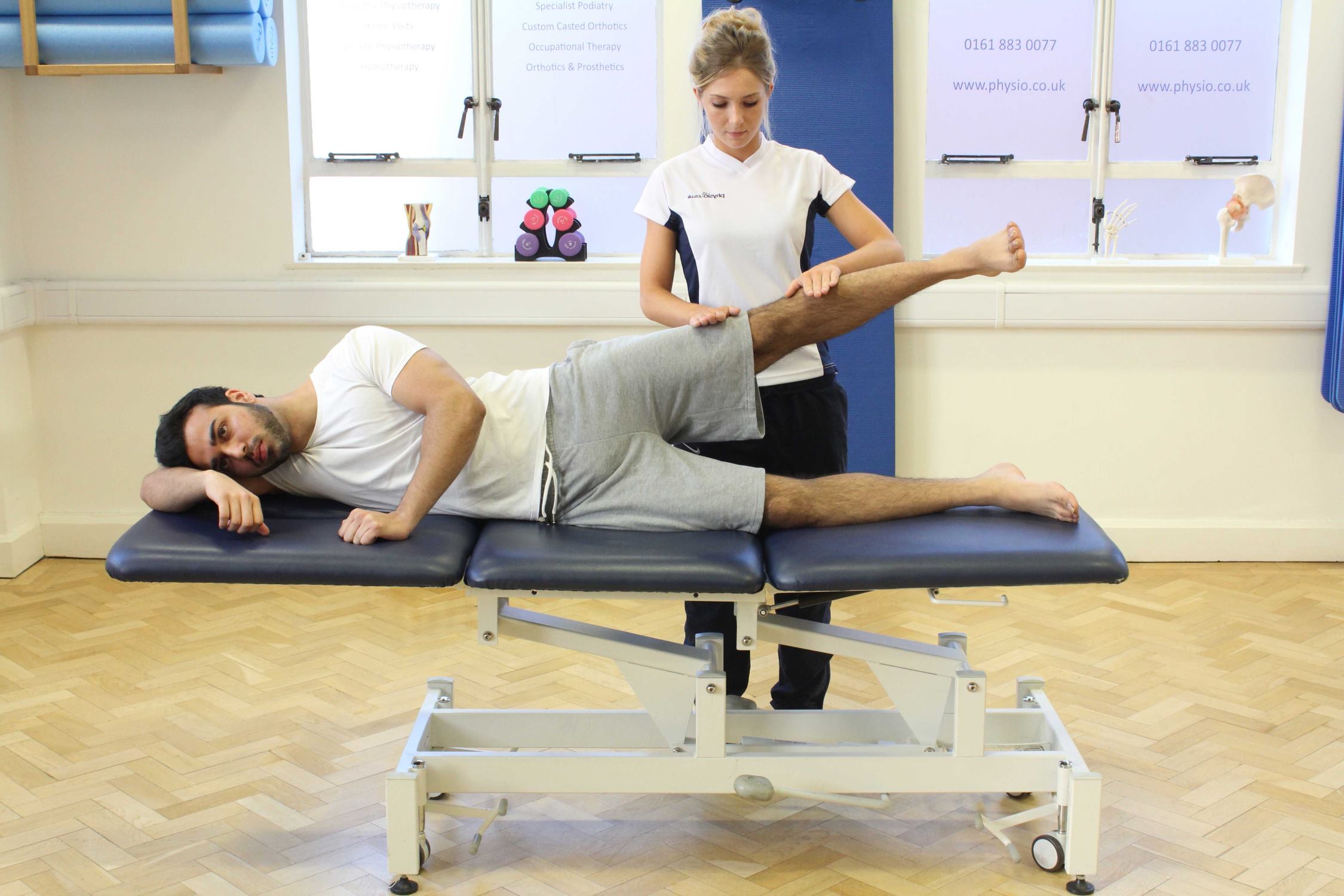
Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in the conservative management of PFPS, focusing on strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip abductor muscles to restore optimal lower limb biomechanics. Therapeutic exercises, such as leg presses, lunges, and hip abduction drills, aim to enhance muscular balance and improve patellar tracking, thereby mitigating the stress on the knee joint during running activities. Additionally, manual therapy techniques, including soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization, can alleviate muscular tightness and enhance joint mobility, fostering a conducive environment for rehabilitation.
Orthotic Intervention
Customized orthotic devices, such as patellar stabilizing braces and foot orthoses, can provide external support and alignment correction, reducing patellar maltracking and alleviating anterior knee pain during running. These orthotic interventions are tailored to the individual's biomechanical needs, addressing specific gait abnormalities and foot alignment issues to optimize running mechanics and minimize the risk of PFPS recurrence.
Pharmacological Management
Pain Management
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics may be prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with PFPS. These medications can offer symptomatic relief, enabling individuals to engage in rehabilitative exercises and gradually resume running activities under the guidance of healthcare providers.
Interventional Procedures
Corticosteroid Injections
In cases of persistent pain and inflammation, corticosteroid injections may be administered under the guidance of a healthcare professional. These injections aim to mitigate localized inflammation and provide temporary relief, facilitating the individual's participation in physical therapy and gradual return to running with reduced discomfort.
Surgical Considerations
Arthroscopic Intervention
In refractory cases of PFPS where conservative measures yield limited improvement, arthroscopic surgery may be considered to address underlying structural abnormalities, such as patellar malalignment or cartilage damage. This minimally invasive procedure aims to realign the patella, remove damaged tissue, and optimize joint mechanics, offering a viable option for runners seeking long-term resolution of PFPS-related symptoms.
By integrating these comprehensive treatment options, healthcare providers can collaborate with runners grappling with PFPS to devise personalized management plans, fostering a seamless transition from rehabilitation to running activities. This holistic approach to PFPS management underscores the importance of individualized care, evidence-based interventions, and ongoing support to empower runners in overcoming the challenges posed by this prevalent knee condition.
Preventing and Managing Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome for Runners
Preventing and managing Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) is paramount for runners aiming to sustain their passion for running while safeguarding their musculoskeletal health. By implementing proactive measures and adopting prudent training practices, runners can mitigate the risk of PFPS and foster long-term resilience in their running pursuits.
Biomechanical Assessment and Gait Analysis
Engaging in a comprehensive biomechanical assessment and gait analysis can provide valuable insights into an individual's running mechanics, foot alignment, and lower limb kinematics. By identifying potential gait abnormalities and biomechanical inefficiencies, runners can collaborate with healthcare providers and running specialists to address modifiable risk factors and optimize their running form. Customized orthotic interventions, such as foot orthoses or motion control footwear, can rectify gait anomalies and reduce excessive stress on the knee joint, thereby mitigating the risk of PFPS.
Strength Training and Cross-Training
Integrating targeted strength training exercises into the running regimen can bolster muscular endurance and enhance lower limb stability, reducing the likelihood of PFPS. Emphasizing exercises that target the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and hip abductor muscles can fortify the knee joint and promote optimal patellar tracking during running activities. Additionally, incorporating cross-training activities, such as swimming, cycling, or yoga, can diversify the training stimulus, mitigate overuse injuries, and foster overall musculoskeletal balance, reducing the risk of PFPS associated with repetitive running motions.
Gradual Progression and Recovery Strategies
Adopting a gradual approach to training progression and incorporating adequate rest intervals is pivotal in preventing overuse injuries, including PFPS. Runners should adhere to structured training plans that integrate progressive mileage increments, recovery days, and tapering periods to minimize the cumulative stress on the knee joint. Implementing post-run recovery strategies, such as foam rolling, stretching, and targeted mobility exercises, can alleviate muscular tightness and promote optimal recovery, reducing the risk of PFPS attributable to training-related strain.
Footwear Selection and Running Surface
Selecting appropriate running footwear tailored to the individual's foot type and gait mechanics is instrumental in optimizing foot and knee alignment, thereby reducing the risk of PFPS. Runners should seek professional guidance to ascertain the most suitable footwear options that offer adequate cushioning, stability, and support, aligning with their running biomechanics. Furthermore, opting for running surfaces with optimal shock absorption, such as rubberized tracks or well-maintained trails, can mitigate the impact on the knee joint, minimizing the risk of PFPS associated with running on hard or uneven surfaces.
Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation
Prioritizing injury prevention strategies, such as regular mobility drills, dynamic warm-ups, and cool-down routines, can fortify the musculoskeletal resilience of runners, reducing the incidence of PFPS. Additionally, promptly addressing any early signs of knee discomfort through targeted rehabilitation measures, such as eccentric strengthening exercises and proprioceptive training, can mitigate the progression of PFPS and expedite the return to pain-free running.
By embracing these preventive measures and integrating them into their running journey, runners can proactively manage the risk of PFPS, fostering a sustainable and gratifying running experience while safeguarding their knee health and overall well-being.
Read more: A Comprehensive Guide To Running Nutrition
Conclusion
In conclusion, Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) poses a significant challenge for runners, often impeding their training progress and diminishing the joy derived from their passion for running. However, by gaining a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted nature of PFPS and embracing proactive measures, runners can navigate this condition with resilience and determination.
The intricate interplay of biomechanical, anatomical, and training-related factors underscores the complexity of PFPS, necessitating a holistic approach to its prevention and management. By recognizing the nuanced symptoms, engaging in comprehensive biomechanical assessments, and integrating targeted strength training and cross-training activities, runners can fortify their musculoskeletal resilience and mitigate the risk of PFPS. Furthermore, prioritizing injury prevention strategies, adopting prudent footwear selection, and embracing gradual training progression can foster a sustainable running experience while safeguarding knee health.
The collaborative partnership between runners, healthcare providers, and running specialists is pivotal in devising personalized management plans tailored to the unique needs of individuals grappling with PFPS. By integrating evidence-based treatment modalities, rehabilitative measures, and lifestyle modifications, runners can embark on a journey of recovery and resilience, gradually resuming their running pursuits with confidence and optimism.
The proactive management of PFPS extends beyond symptom alleviation, encompassing a commitment to long-term musculoskeletal health and injury prevention. By embracing a multifaceted approach to PFPS, runners can cultivate a profound sense of empowerment, transcending the challenges posed by this prevalent knee condition and fostering a gratifying and enduring running experience.
In essence, PFPS, though formidable, is not insurmountable. With unwavering dedication, informed decision-making, and a steadfast commitment to injury prevention, runners can transcend the limitations imposed by PFPS, reclaiming the joy and fulfillment inherent in their running endeavors. By embracing the journey of resilience and renewal, runners can forge a path towards sustained musculoskeletal health, enabling them to pursue their passion for running with unwavering vitality and determination.












