Home>Health & Nutrition>Understanding The Purpose Of A Sweat Test

Health & Nutrition
Understanding The Purpose Of A Sweat Test
Published: February 25, 2024
Learn about the importance of sweat tests in assessing health and nutrition. Understand how this diagnostic tool can provide valuable insights into your overall well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The human body is a marvel of complexity, constantly engaged in a multitude of processes to maintain optimal health. One such process, often overlooked in everyday discussions about health, is sweating. While sweating is commonly associated with physical exertion or warm temperatures, it serves a crucial physiological purpose beyond cooling the body. The analysis of sweat, through a diagnostic procedure known as a sweat test, provides valuable insights into the functioning of the body's sweat glands and can aid in the diagnosis of certain medical conditions.
The sweat test is a non-invasive procedure that involves collecting a small sample of sweat to measure the concentration of chloride and sodium, among other substances. These measurements can provide healthcare professionals with essential information about the body's ability to regulate salt and water, offering valuable clues about the presence of certain medical conditions.
Understanding the purpose of a sweat test is essential for appreciating its significance in the realm of healthcare. This diagnostic tool plays a pivotal role in the identification of conditions such as cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder that affects the lungs and digestive system. By comprehending the intricacies of the sweat test, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of its role in diagnosing and managing various health conditions.
The following sections will delve into the specifics of the sweat test, including its procedure, the conditions that necessitate its use, and the significance of interpreting its results. By exploring these aspects, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the importance of the sweat test in the realm of medical diagnostics.
Read more: Experience The VO2-max Test For Yourself
What is a Sweat Test?
A sweat test is a diagnostic procedure designed to measure the concentration of chloride and sodium in sweat. This non-invasive test provides valuable insights into the functioning of the sweat glands and the body's ability to maintain proper salt and water balance. The test is commonly used to diagnose cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder that affects the respiratory and digestive systems.
During a sweat test, a small area of the skin, typically on the forearm, is stimulated to produce sweat. The collected sweat is then analyzed to determine the levels of chloride and sodium. This process is crucial in identifying abnormalities in the sweat composition, which can indicate underlying health conditions.
The measurement of chloride and sodium in sweat is particularly significant in the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Individuals with cystic fibrosis often have abnormally high levels of chloride in their sweat due to the malfunctioning of the sweat glands. By detecting elevated chloride levels through a sweat test, healthcare professionals can initiate further diagnostic evaluations and provide timely interventions for affected individuals.
In addition to cystic fibrosis, sweat tests can also aid in the diagnosis of other conditions, such as certain types of salt-losing tubulopathies and congenital adrenal hyperplasia. These tests play a crucial role in identifying underlying health issues, enabling healthcare providers to formulate appropriate treatment plans and support patients in managing their conditions effectively.
Overall, the sweat test serves as a valuable tool in the realm of medical diagnostics, offering crucial insights into the body's physiological processes. By understanding the fundamentals of the sweat test, individuals can appreciate its significance in identifying and managing various health conditions, ultimately contributing to improved healthcare outcomes for affected individuals.
How is a Sweat Test Performed?
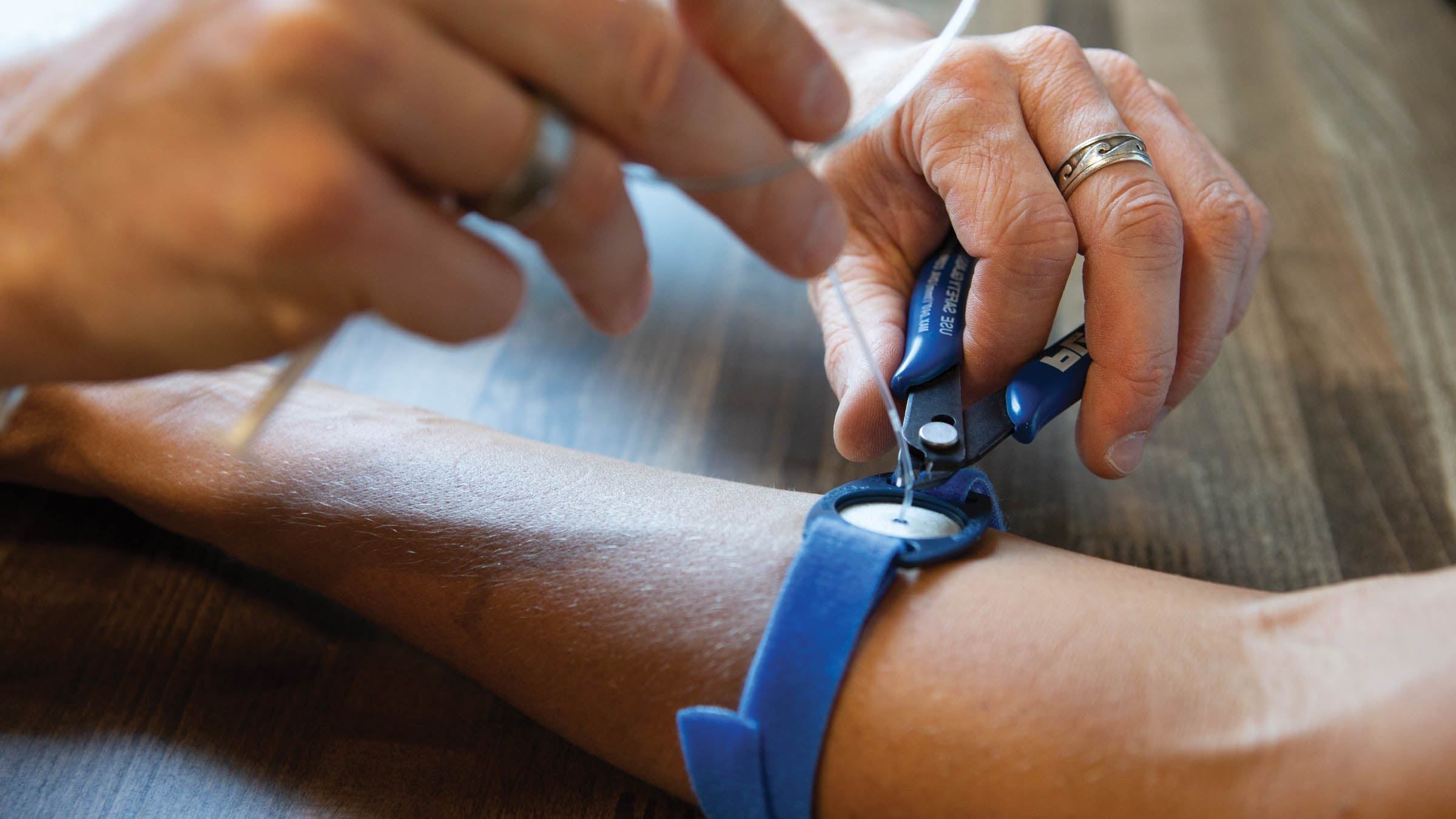
A sweat test is a meticulously conducted diagnostic procedure that involves the collection and analysis of sweat to assess the levels of chloride and sodium. The process begins with the selection of an appropriate site for sweat stimulation, typically the forearm. The chosen area is cleansed to ensure the accuracy of the test results, as any external contaminants could compromise the validity of the analysis.
Once the skin is prepared, a chemical known as pilocarpine is applied to the site. Pilocarpine acts as a sweat stimulant, effectively prompting the sweat glands to produce perspiration. To facilitate this process, a small, painless electric current may be used to stimulate sweat production in the targeted area. The duration of sweat collection varies, typically lasting between 30 and 60 minutes, during which the individual may engage in quiet activities to pass the time.
Following the collection period, the sweat is carefully gathered using a specialized device, such as a sweat collection coil or absorbent pad, to ensure accurate sample acquisition. The collected sweat is then transferred to a laboratory for analysis. In the laboratory setting, the sweat sample undergoes meticulous examination to determine the concentrations of chloride and sodium, along with other relevant substances.
The analysis involves precise techniques to measure the levels of chloride and sodium in the sweat sample. This process may utilize methods such as ion-selective electrodes or coulometric titration, both of which are designed to provide accurate and reliable results. The obtained measurements are then compared to established reference ranges to assess the composition of the sweat and identify any deviations from normal values.
The results of the sweat test play a crucial role in the diagnosis of various medical conditions, particularly cystic fibrosis. Elevated chloride levels in the sweat can indicate the presence of cystic fibrosis, prompting further diagnostic evaluations to confirm the diagnosis. Additionally, the sweat test can aid in the identification of other conditions characterized by abnormalities in sweat composition, enabling healthcare providers to initiate appropriate interventions and support individuals in managing their health effectively.
In essence, the sweat test is a meticulously orchestrated procedure that yields valuable insights into the body's physiological processes. By understanding the intricacies of how a sweat test is performed, individuals can appreciate the significance of this diagnostic tool in identifying and managing a range of health conditions.
Conditions that Require a Sweat Test
The sweat test serves as a pivotal diagnostic tool in the assessment of various medical conditions, particularly those related to salt and water balance and sweat gland function. One of the primary conditions that necessitate a sweat test is cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder that affects multiple organ systems, most notably the respiratory and digestive systems. Cystic fibrosis is characterized by the production of thick, sticky mucus that can obstruct the airways and impair digestive processes. The sweat test plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis, as individuals with this condition often exhibit abnormally high levels of chloride in their sweat due to the malfunctioning of the sweat glands.
In addition to cystic fibrosis, certain types of salt-losing tubulopathies and congenital adrenal hyperplasia may also warrant the use of a sweat test for diagnostic purposes. Salt-losing tubulopathies encompass a group of rare genetic disorders that affect the kidneys' ability to reabsorb salt, leading to excessive salt loss in the urine. These conditions can result in electrolyte imbalances and dehydration, necessitating the evaluation of sweat composition to assess salt handling by the body.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a group of inherited disorders affecting the adrenal glands, can also prompt the need for a sweat test. This condition involves deficiencies in the production of certain hormones, particularly cortisol, which can impact salt and water balance in the body. By analyzing the sweat composition, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into the body's ability to regulate salt levels, aiding in the diagnosis and management of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Furthermore, the sweat test may be utilized in the assessment of individuals with suspected pseudohypoaldosteronism, a rare condition characterized by salt wasting and high levels of sodium in the urine. The test can help identify abnormalities in sweat electrolyte levels, contributing to the comprehensive evaluation of salt and water balance in affected individuals.
Overall, the sweat test plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of various conditions related to salt and water balance, providing healthcare providers with essential information to guide diagnostic evaluations and formulate appropriate treatment plans. By recognizing the significance of the sweat test in the context of these conditions, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of its role in identifying and managing health challenges related to salt and water regulation.
Interpreting the Results of a Sweat Test
Upon completion of a sweat test, the obtained results undergo meticulous analysis to interpret the composition of the sweat and derive valuable insights into the body's physiological processes. The interpretation of the sweat test results is a critical aspect of the diagnostic process, particularly in the context of identifying conditions such as cystic fibrosis and other disorders related to salt and water balance.
The primary focus of interpreting the results revolves around the concentrations of chloride and sodium in the sweat sample. Elevated levels of chloride in the sweat, typically exceeding 60 millimoles per liter, are indicative of abnormal salt transport in the sweat glands. This finding is particularly significant in the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis, as individuals with this condition often exhibit excessively high chloride levels due to the malfunctioning of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein. The presence of elevated chloride levels in the sweat prompts further diagnostic evaluations to confirm the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis, enabling healthcare providers to initiate timely interventions and support affected individuals effectively.
In addition to chloride, the measurement of sodium levels in the sweat sample provides valuable complementary information. While sodium levels alone may not be as specific for cystic fibrosis diagnosis, they contribute to the comprehensive assessment of sweat composition. The interpretation of sodium levels in conjunction with chloride concentrations enhances the diagnostic accuracy, particularly in differentiating between cystic fibrosis and other conditions that may affect sweat electrolyte balance.
Furthermore, the interpretation of sweat test results extends beyond chloride and sodium measurements to encompass other relevant substances, such as potassium and conductivity. These additional parameters contribute to a comprehensive evaluation of sweat composition, offering valuable insights into the body's electrolyte balance and sweat gland function.
Overall, the interpretation of sweat test results is a nuanced process that involves meticulous analysis of chloride, sodium, and other relevant substances in the sweat sample. By accurately interpreting the results, healthcare providers can gain crucial insights into the body's salt and water regulation, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various medical conditions. The significance of interpreting sweat test results lies in its role as a cornerstone of diagnostic evaluations, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions and support individuals in managing their health effectively.
Read more: Understanding The Concept Of A Tempo Run
Importance of a Sweat Test in Diagnosis
The sweat test holds immense significance in the realm of medical diagnosis, serving as a pivotal tool in the identification and management of various health conditions. One of the primary areas where the sweat test demonstrates its importance is in the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder that affects multiple organ systems, particularly the respiratory and digestive systems. Individuals with cystic fibrosis often exhibit abnormally high levels of chloride in their sweat due to the malfunctioning of the sweat glands. As such, the sweat test plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis, enabling healthcare providers to initiate timely interventions and support affected individuals effectively.
Beyond cystic fibrosis, the sweat test contributes to the diagnosis of other conditions related to salt and water balance and sweat gland function. Certain types of salt-losing tubulopathies, characterized by excessive salt loss in the urine due to kidney abnormalities, may necessitate the use of a sweat test to assess the body's salt handling capacity. Additionally, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a group of inherited disorders affecting hormone production in the adrenal glands, can prompt the need for a sweat test to evaluate salt and water balance. The test also aids in the assessment of individuals with suspected pseudohypoaldosteronism, a rare condition involving salt wasting and high levels of sodium in the urine.
The importance of the sweat test in diagnosis extends beyond the identification of specific conditions to encompass the comprehensive evaluation of salt and water regulation in the body. By analyzing sweat composition, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into the body's physiological processes, aiding in the formulation of appropriate treatment plans and supportive interventions for affected individuals. The test serves as a cornerstone of diagnostic evaluations, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions and support individuals in managing their health effectively.
In essence, the sweat test holds immense importance in the diagnosis of various medical conditions, offering valuable insights into the body's salt and water balance and sweat gland function. By recognizing the significance of the sweat test in the context of diagnosis, individuals and healthcare professionals can appreciate its role in identifying and managing health challenges related to salt and water regulation, ultimately contributing to improved healthcare outcomes for affected individuals.
Potential Risks and Limitations of a Sweat Test
While the sweat test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it is essential to acknowledge the potential risks and limitations associated with this procedure. Understanding these aspects is crucial for both healthcare providers and individuals undergoing the test, as it allows for informed decision-making and comprehensive evaluation of its implications.
One of the primary considerations regarding the sweat test is the potential for skin irritation at the site of sweat stimulation. The application of pilocarpine, a sweat stimulant commonly used in the test, may cause mild skin redness or discomfort in some individuals. However, these effects are typically transient and resolve shortly after the completion of the test. Healthcare providers ensure that the chosen site for sweat stimulation is carefully monitored to minimize the risk of skin irritation and address any discomfort experienced by the individual.
Another aspect to consider is the duration of sweat collection, which can range from 30 to 60 minutes. While the process is generally well-tolerated, individuals undergoing the test may experience mild discomfort or restlessness during the collection period. Healthcare providers strive to create a comfortable and supportive environment for individuals undergoing the sweat test, addressing any concerns and ensuring that the process is conducted with minimal disruption to the individual's well-being.
In addition to potential discomfort during the test, it is important to recognize the limitations of the sweat test in certain scenarios. While the test is highly valuable in diagnosing conditions such as cystic fibrosis and assessing salt and water balance, it is not infallible. In some cases, technical challenges or individual variations in sweat production may affect the accuracy of the test results. Healthcare providers carefully consider these factors and may utilize complementary diagnostic approaches to corroborate the findings of the sweat test, ensuring a comprehensive and accurate assessment of the individual's health status.
Furthermore, the interpretation of sweat test results requires a nuanced understanding of the physiological processes involved. While elevated chloride levels in the sweat are indicative of certain conditions, including cystic fibrosis, the interpretation of results necessitates careful consideration of various factors, such as age, medications, and individual variability. Healthcare providers leverage their expertise to accurately interpret sweat test results, accounting for these nuances and ensuring that the findings align with the individual's clinical presentation and medical history.
Overall, while the sweat test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it is essential to acknowledge the potential risks, discomfort, and limitations associated with the procedure. By recognizing these aspects, healthcare providers can ensure the well-being of individuals undergoing the test and make informed decisions regarding its use in diagnostic evaluations. Additionally, individuals can approach the sweat test with a comprehensive understanding of its implications, fostering a collaborative and supportive approach to healthcare management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sweat test stands as a remarkable diagnostic tool that offers valuable insights into the body's physiological processes, particularly in relation to salt and water regulation and sweat gland function. Through the meticulous collection and analysis of sweat, healthcare providers can gain crucial information to aid in the diagnosis and management of various medical conditions.
The significance of the sweat test is particularly evident in the context of cystic fibrosis, where elevated chloride levels in the sweat serve as a hallmark indicator of the condition. By promptly identifying abnormal sweat composition through the sweat test, healthcare providers can initiate timely interventions and support affected individuals effectively, ultimately contributing to improved health outcomes.
Furthermore, the sweat test plays a pivotal role in the assessment of other conditions related to salt and water balance, such as certain types of salt-losing tubulopathies and congenital adrenal hyperplasia. By evaluating sweat composition, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into the body's ability to regulate salt levels, enabling comprehensive diagnostic evaluations and the formulation of appropriate treatment plans.
While the sweat test offers immense diagnostic value, it is essential to recognize its potential risks and limitations, including the possibility of mild skin irritation and the need for careful interpretation of results. By acknowledging these aspects, healthcare providers can ensure the well-being of individuals undergoing the test and make informed decisions regarding its use in diagnostic evaluations.
Overall, the sweat test stands as a cornerstone of diagnostic assessments, providing essential information to guide healthcare interventions and support individuals in managing their health effectively. By understanding the purpose and significance of the sweat test, individuals and healthcare professionals can collaborate to harness its diagnostic potential, ultimately contributing to enhanced healthcare outcomes and improved quality of life for affected individuals.