Home>Health & Nutrition>Injury Prevention>Understanding Foot Cramps: The Causes Of Foot Cramps While Running

Injury Prevention
Understanding Foot Cramps: The Causes Of Foot Cramps While Running
Published: February 25, 2024
Learn how to prevent foot cramps while running. Discover the causes and effective injury prevention techniques. Keep your feet pain-free during your runs.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Foot cramps while running can be a frustrating and painful experience for many athletes and fitness enthusiasts. These sudden, involuntary muscle contractions in the foot can disrupt a workout or even lead to injuries if not addressed properly. Understanding the causes of foot cramps while running is crucial for preventing and managing this discomfort.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the anatomy of the foot, explore the common causes of foot cramps while running, discuss effective prevention and treatment strategies, and highlight the importance of seeking medical attention when necessary. Whether you are a seasoned runner or just starting your fitness journey, this article will equip you with valuable insights to help you overcome foot cramps and optimize your running experience.
Let's embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries behind foot cramps while running and empower ourselves with the knowledge to conquer this common challenge.
The Anatomy of the Foot
The foot is a complex structure comprising bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves, all working in harmony to support the body's weight and facilitate movement. Understanding the intricate anatomy of the foot is essential for comprehending the potential causes of foot cramps while running.
Bones and Joints
The foot consists of 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. These bones form the arches of the foot, providing stability and flexibility. The joints in the foot, such as the ankle joint and the numerous smaller joints in the midfoot and forefoot, enable a wide range of movements essential for walking, running, and other weight-bearing activities.
Muscles and Tendons
A network of intrinsic and extrinsic muscles in the foot and lower leg work together to control movement and provide support. The intrinsic muscles, located within the foot, play a crucial role in maintaining the arches and stabilizing the toes during propulsion. Meanwhile, the extrinsic muscles, originating from the lower leg, extend into the foot via tendons, contributing to overall foot function and mobility.
Ligaments and Connective Tissues
Ligaments are strong bands of connective tissue that connect bones to each other, providing stability to the joints. The foot's ligaments, including the plantar fascia and various collateral ligaments, help maintain the arches and support the foot's structure during weight-bearing activities. Additionally, the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue running along the bottom of the foot, plays a pivotal role in absorbing shock and maintaining the foot's arches.
Nerves and Blood Supply
The foot is richly innervated, with numerous nerves responsible for transmitting sensory information and controlling muscle movements. The proper functioning of these nerves is essential for maintaining balance, coordination, and proprioception. Furthermore, a robust network of blood vessels ensures adequate blood supply to the foot, delivering oxygen and nutrients while facilitating the removal of metabolic waste products.
By gaining a deeper understanding of the intricate interplay between these anatomical components, we can better appreciate the potential factors that contribute to foot cramps while running. This knowledge forms the foundation for addressing and mitigating the discomfort associated with foot cramps, ultimately enhancing the overall running experience.
Common Causes of Foot Cramps While Running
-
Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake before, during, or after running can lead to dehydration, disrupting the body's electrolyte balance and increasing the likelihood of foot cramps.
-
Electrolyte Imbalance: The depletion of essential electrolytes, such as potassium, magnesium, and sodium, due to excessive sweating during prolonged runs can trigger muscle cramps in the feet.
-
Muscle Fatigue: Overexertion and prolonged physical activity can lead to muscle fatigue, causing the muscles in the feet to involuntarily contract and spasm, resulting in cramps.
-
Improper Footwear: Wearing ill-fitting or worn-out running shoes can contribute to foot cramps by altering the foot's biomechanics and placing excessive stress on certain muscles and tendons.
-
Poor Running Technique: Inefficient running form, such as overstriding or excessive pronation, can place undue strain on the foot muscles, leading to cramping during or after a run.
-
Inadequate Warm-Up: Failing to properly warm up before running can leave the foot muscles unprepared for the demands of physical activity, increasing the risk of cramps.
-
Tight or Weak Muscles: Muscular imbalances, tightness in the calf muscles, or weakness in the foot muscles can predispose individuals to foot cramps while running.
-
Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as peripheral artery disease, nerve compression syndromes, or metabolic disorders, may manifest as foot cramps during physical exertion.
Understanding these common causes of foot cramps while running empowers individuals to take proactive measures to mitigate the risk of experiencing this discomfort. By addressing these factors through proper hydration, adequate nutrition, appropriate footwear, and targeted strength and flexibility exercises, runners can significantly reduce the incidence of foot cramps and enjoy a more rewarding and pain-free running experience.
Prevention and Treatment of Foot Cramps
Preventing and effectively managing foot cramps while running is essential for maintaining optimal performance and minimizing discomfort. By implementing proactive strategies and adopting targeted treatment approaches, individuals can significantly reduce the incidence of foot cramps and alleviate their symptoms when they occur.
Prevention Strategies
-
Hydration: Adequate hydration is crucial for preventing foot cramps. Maintaining a proper fluid balance by consuming water before, during, and after running helps sustain electrolyte levels and muscle function.
-
Electrolyte Balance: Incorporating electrolyte-rich foods, such as bananas, leafy greens, and nuts, into the diet can help prevent imbalances that contribute to muscle cramping.
-
Proper Footwear: Investing in well-fitting, supportive running shoes that suit individual biomechanics and foot structure is vital for preventing foot cramps. Additionally, replacing worn-out shoes in a timely manner is essential for maintaining optimal foot support.
-
Warm-Up and Cool Down: Engaging in dynamic warm-up exercises before running and incorporating post-run stretching and cool-down routines can prepare the foot muscles for activity and aid in preventing cramps.
-
Strength and Flexibility Training: Implementing targeted strength and flexibility exercises for the feet, ankles, and lower legs can help address muscular imbalances and enhance overall foot function, reducing the risk of cramping.
Treatment Approaches
-
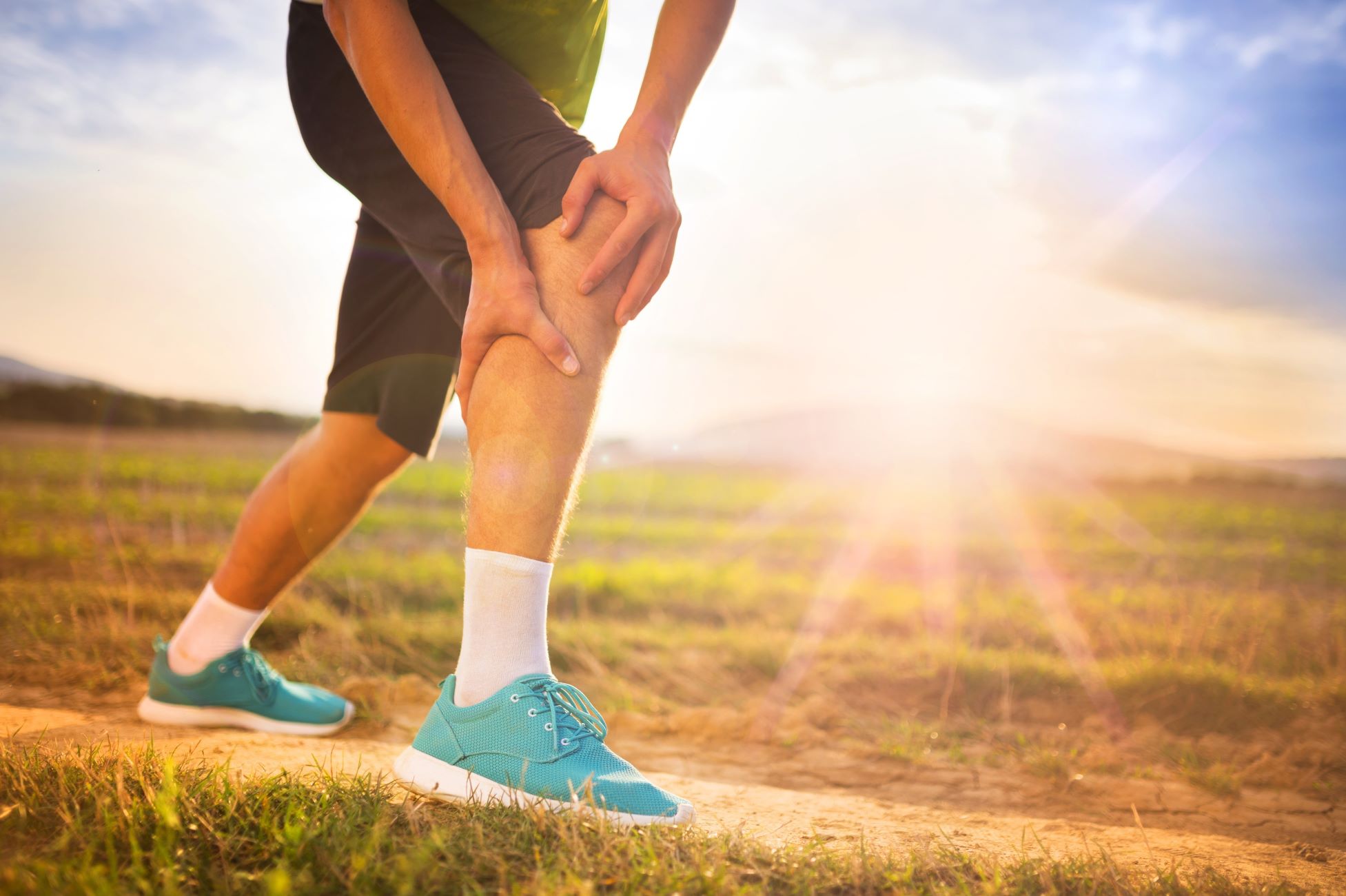
Immediate Relief: When a foot cramp occurs during a run, stopping to stretch and massage the affected area can provide immediate relief. Gently flexing and extending the toes and massaging the cramped muscles can help alleviate the cramp.
-
Hydration and Nutrition: Rehydrating and replenishing electrolytes post-cramp is essential for restoring the body's balance. Consuming a balanced meal or snack containing potassium, magnesium, and sodium can aid in recovery.
-
RICE Method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation can be beneficial for managing post-run foot cramps. Applying ice, gentle compression, and elevating the affected foot can help reduce inflammation and discomfort.
-
Foot Massage and Stretching: Regularly massaging the feet and incorporating stretching exercises targeting the calf muscles, plantar fascia, and toes can help alleviate tension and prevent cramps.
-
Professional Evaluation: If foot cramps persist despite preventive measures and self-care, seeking professional evaluation from a healthcare provider or a sports medicine specialist is advisable to identify any underlying issues and receive tailored treatment recommendations.
By integrating these preventive measures and treatment approaches into their running routine, individuals can proactively address foot cramps and foster a more enjoyable and rewarding running experience.
When to Seek Medical Attention
In some instances, foot cramps while running may persist despite implementing preventive measures and self-care strategies. When individuals experience recurrent or severe foot cramps that significantly impact their running performance and overall well-being, seeking medical attention becomes imperative.
Persistent foot cramps could be indicative of underlying issues that require professional evaluation and targeted intervention. If the foot cramps are accompanied by symptoms such as persistent pain, swelling, numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider or a sports medicine specialist.
Furthermore, individuals with a history of chronic foot cramps or those who notice a sudden onset of cramping unrelated to physical activity should consider seeking medical assessment. This is particularly important for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions such as diabetes, peripheral artery disease, or neurological disorders, as these conditions can contribute to foot cramping and require specialized management.
Moreover, if foot cramps interfere with daily activities, affect sleep quality, or persist despite adequate hydration, nutrition, and footwear adjustments, it is advisable to seek medical attention. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional can help identify any underlying anatomical, biomechanical, or neurological factors contributing to the foot cramps and guide the implementation of targeted treatment strategies.
In summary, recognizing the signs that warrant medical attention for foot cramps while running is essential for ensuring comprehensive care and addressing any potential underlying issues. By promptly seeking professional evaluation and guidance, individuals can receive personalized recommendations to effectively manage foot cramps and optimize their running experience.