Home>Health & Nutrition>Injury Prevention>4 Common Foot Injuries To Be Aware Of When Running

Injury Prevention
4 Common Foot Injuries To Be Aware Of When Running
Published: February 26, 2024
Learn about 4 common foot injuries to watch out for when running and how to prevent them. Protect your feet with injury prevention tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
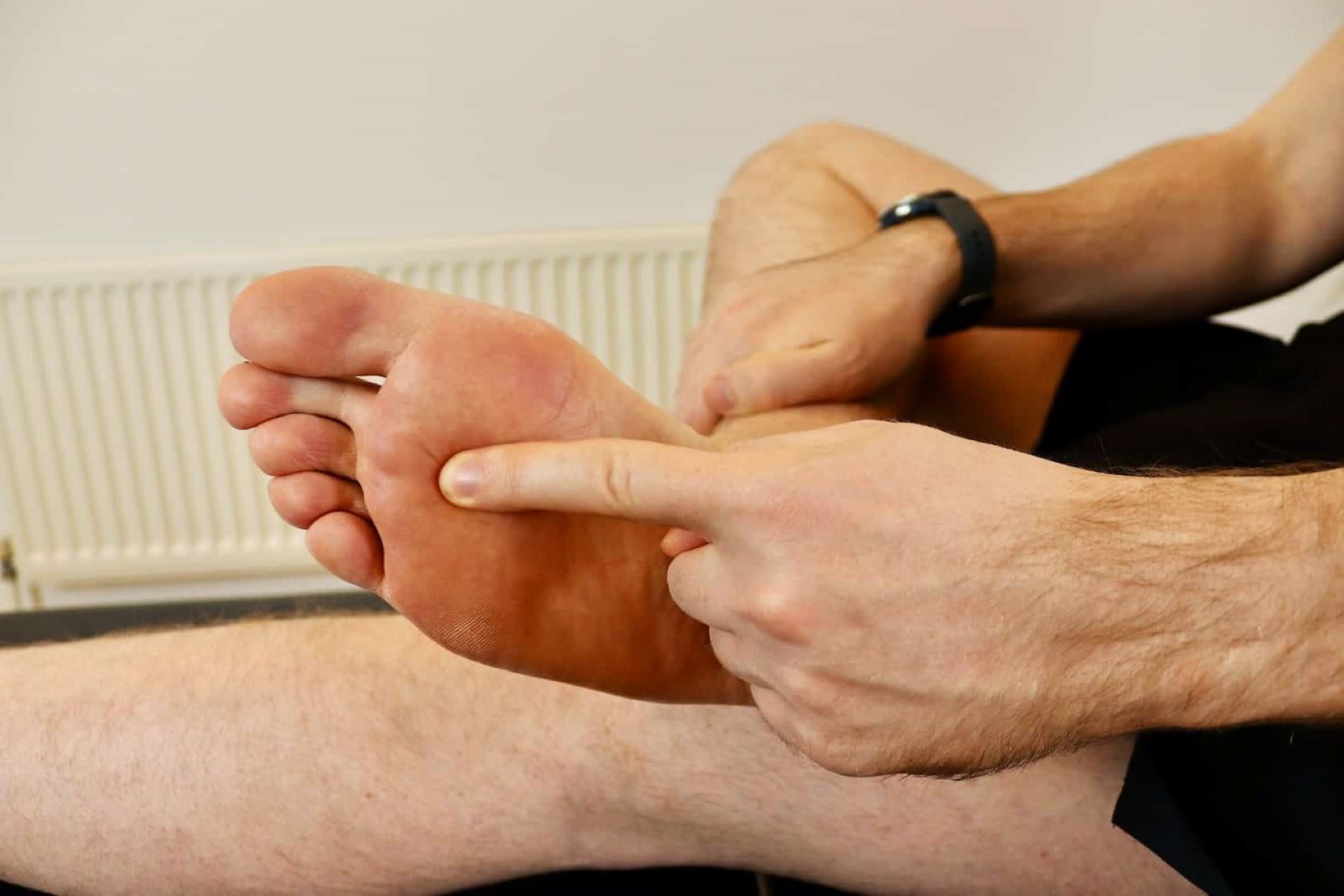
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a prevalent foot injury that can afflict runners, causing discomfort and hindering performance. This condition occurs when the plantar fascia, a band of tissue connecting the heel bone to the toes, becomes inflamed or strained. The plantar fascia plays a crucial role in supporting the arch of the foot and absorbing the impact of each step during running. However, repetitive stress or overuse can lead to micro-tears and inflammation in this tissue, resulting in the characteristic heel pain associated with plantar fasciitis.
Read more: 4 Common Causes Of Knee Pain After Running
Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of plantar fasciitis is a sharp, stabbing pain in the heel, particularly upon taking the first steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest. This discomfort may gradually diminish as the foot limbers up, only to return after extended periods of standing or physical activity. Furthermore, individuals with plantar fasciitis may experience heightened pain after running, jumping, or climbing stairs.
Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis, including excessive running or sudden increases in training intensity, inadequate footwear, high arches or flat feet, and tight calf muscles. Additionally, obesity, which places added stress on the plantar fascia, can elevate the risk of developing this condition.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing plantar fasciitis involves incorporating proper foot care and injury prevention strategies into one's running routine. This includes wearing supportive, well-cushioned footwear, gradually increasing training intensity, and incorporating stretching exercises to enhance flexibility and reduce strain on the plantar fascia. Moreover, maintaining a healthy body weight and cross-training to minimize repetitive impact on the feet can also aid in preventing this condition.
In terms of treatment, rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate the discomfort associated with plantar fasciitis. Additionally, physical therapy, orthotic inserts, and night splints may be recommended to support the foot and facilitate healing. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or extracorporeal shock wave therapy may be considered to address persistent symptoms.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures associated with plantar fasciitis is crucial for runners aiming to safeguard their foot health and overall well-being. By prioritizing proper footwear, gradual training progression, and proactive injury management, individuals can minimize the risk of developing this debilitating condition and continue pursuing their running goals with confidence.
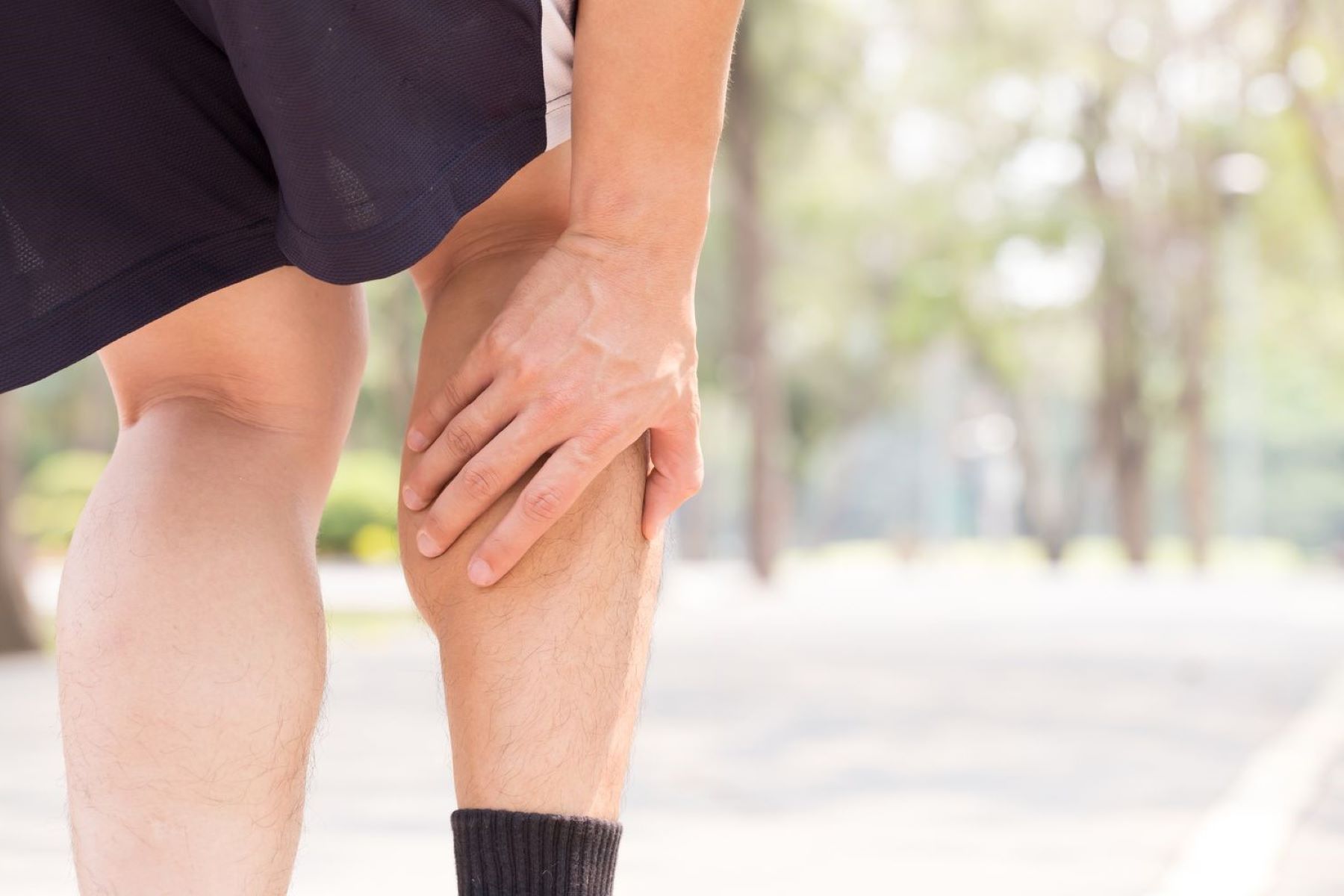
Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis, a prevalent injury among runners, occurs when the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone, becomes inflamed due to overuse or strain. This vital tendon plays a pivotal role in facilitating movement, particularly during activities such as running, jumping, and walking. However, repetitive stress or sudden increases in physical activity can lead to micro-tears and inflammation in the Achilles tendon, resulting in discomfort and potential impairment of mobility.
Read more: 4 Common Causes Of Knee Pain After Running
Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of Achilles tendonitis is pain and stiffness in the tendon, particularly in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest. This discomfort may escalate during physical activity, such as running or climbing stairs, and can be accompanied by swelling or tenderness in the affected area. Furthermore, individuals with Achilles tendonitis may experience a noticeable thickening of the tendon and difficulty flexing the foot or standing on tiptoes.
Causes
Several factors contribute to the development of Achilles tendonitis, including excessive running or sudden increases in training intensity, inadequate footwear, tight calf muscles, and biomechanical issues such as overpronation. Additionally, engaging in activities that involve repetitive stress on the Achilles tendon, such as running on uneven surfaces or wearing worn-out shoes, can elevate the risk of developing this condition.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing Achilles tendonitis involves implementing proactive measures to safeguard the health and integrity of the Achilles tendon. This includes incorporating proper warm-up and cool-down routines into one's exercise regimen, wearing supportive footwear with adequate cushioning, and gradually increasing training intensity to minimize strain on the tendon. Moreover, performing strengthening and stretching exercises targeting the calf muscles and Achilles tendon can enhance flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
In terms of treatment, rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate the discomfort associated with Achilles tendonitis. Additionally, physical therapy, eccentric strengthening exercises, and orthotic inserts may be recommended to support the tendon and promote healing. In severe cases, immobilization in a walking boot or the use of a heel lift to reduce tension on the tendon may be necessary to facilitate recovery.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures associated with Achilles tendonitis is crucial for runners aiming to protect their foot health and overall well-being. By prioritizing proper warm-up routines, gradual training progression, and proactive injury management, individuals can minimize the risk of developing this debilitating condition and continue pursuing their running goals with confidence.
Stress Fractures
Stress fractures are a common concern for runners, characterized by small cracks or severe bruising within the bone. These injuries often result from repetitive stress and overuse, particularly in the weight-bearing bones of the lower extremities, such as the shins, feet, and hips. The constant impact and strain placed on the bones during running can lead to the gradual development of stress fractures, causing discomfort and potentially impeding one's running performance.
Read more: 4 Common Causes Of Knee Pain After Running
Symptoms
The symptoms of stress fractures may manifest as localized pain and tenderness, often exacerbated during weight-bearing activities such as running or jumping. Individuals may experience swelling around the affected area, and in some cases, there may be visible bruising. Moreover, the discomfort associated with stress fractures tends to intensify during physical activity and diminish with rest, only to resurface upon resuming weight-bearing exercises.
Causes
Several factors contribute to the development of stress fractures, including sudden increases in training intensity, inadequate footwear, and biomechanical issues such as overpronation or flat feet. Additionally, nutritional deficiencies, particularly in calcium and vitamin D, can compromise bone strength and increase the susceptibility to stress fractures. Furthermore, engaging in high-impact activities on hard surfaces or abruptly changing one's exercise routine can elevate the risk of developing these debilitating injuries.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing stress fractures involves implementing proactive measures to fortify bone health and minimize the risk of injury. This includes gradually increasing training intensity, incorporating cross-training activities to reduce repetitive stress on the bones, and ensuring proper nutrition to support bone strength and repair. Moreover, wearing supportive footwear with adequate cushioning and shock absorption can help mitigate the impact on the bones during running, thereby reducing the risk of stress fractures.
In terms of treatment, rest and modified physical activity are essential for allowing the affected bones to heal. Additionally, applying ice to the affected area and elevating the leg can help alleviate swelling and discomfort. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the appropriate course of treatment, which may include the use of crutches, protective footwear, or in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures associated with stress fractures is crucial for runners aiming to safeguard their bone health and overall well-being. By prioritizing gradual training progression, proper nutrition, and proactive injury management, individuals can minimize the risk of developing stress fractures and continue pursuing their running goals with confidence.
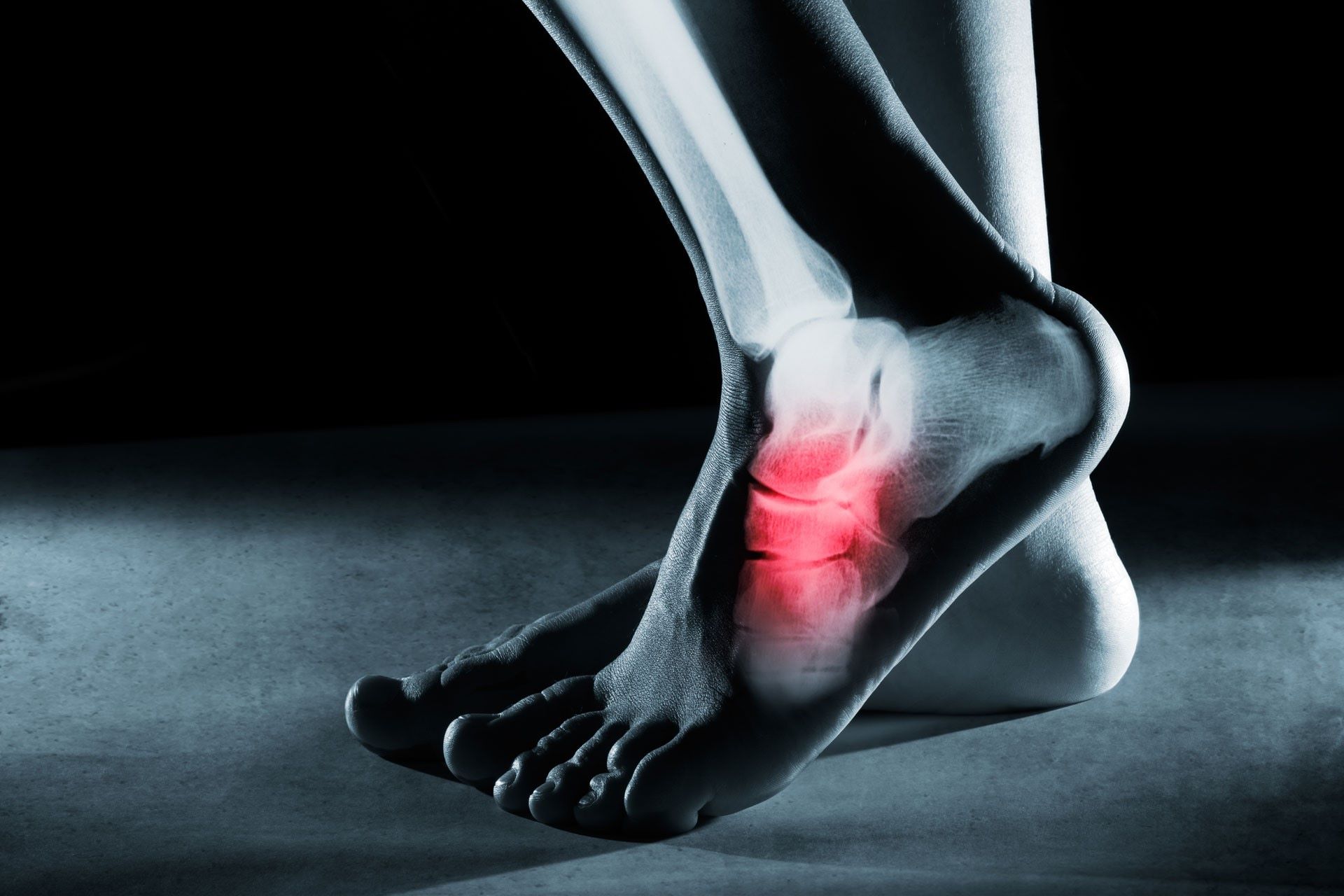
Ankle Sprains
Ankle sprains are a prevalent injury among runners, often resulting from sudden twisting or rolling of the ankle joint beyond its normal range of motion. This can lead to stretching or tearing of the ligaments that support the ankle, causing discomfort and potential impairment of mobility. The lateral ligaments, located on the outer aspect of the ankle, are particularly susceptible to injury during running, especially when navigating uneven terrain or encountering unexpected obstacles.
Read more: 4 Common Causes Of Knee Pain After Running
Symptoms
The symptoms of an ankle sprain typically include pain, swelling, and bruising around the affected area. Individuals may experience difficulty bearing weight on the injured ankle and may notice instability or a feeling of "giving way" when attempting to stand or walk. Furthermore, the discomfort associated with ankle sprains tends to intensify during weight-bearing activities and may be accompanied by a noticeable decrease in range of motion.
Causes
Ankle sprains often occur when the foot lands unevenly on the ground, causing the ankle to roll inward or outward abruptly. This can strain or tear the ligaments, leading to the characteristic symptoms of an ankle sprain. Factors such as running on uneven surfaces, wearing unsupportive footwear, and muscle weakness or imbalance in the lower extremities can increase the risk of sustaining an ankle sprain during running. Additionally, inadequate warm-up or insufficient flexibility in the ankle joint can also contribute to the likelihood of injury.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing ankle sprains involves implementing proactive measures to strengthen the ankle and minimize the risk of injury. This includes incorporating balance and proprioception exercises into one's training regimen to enhance ankle stability and reduce the likelihood of sudden twists or rolls. Moreover, wearing supportive footwear with proper ankle support and adequate cushioning can help mitigate the risk of ankle sprains during running.
In terms of treatment, the R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) protocol is commonly recommended to alleviate the discomfort and swelling associated with ankle sprains. Additionally, performing gentle range-of-motion exercises and gradually reintroducing weight-bearing activities can aid in restoring mobility and function to the injured ankle. It is essential to seek professional medical evaluation to determine the severity of the sprain and to receive appropriate guidance on rehabilitation and recovery.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures associated with ankle sprains is crucial for runners aiming to protect their foot health and overall well-being. By prioritizing ankle strengthening exercises, proper footwear, and proactive injury management, individuals can minimize the risk of sustaining ankle sprains and continue pursuing their running goals with confidence.