Home>Health & Nutrition>Injury Prevention>Experiencing Foot Pain Post-run? Consider Morton’s Neuroma As A Possible Cause

Injury Prevention
Experiencing Foot Pain Post-run? Consider Morton’s Neuroma As A Possible Cause
Published: February 26, 2024
Experiencing foot pain after running? Learn about Morton's neuroma as a potential cause and how to prevent this injury. Find helpful tips for injury prevention.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Morton's Neuroma
Morton's neuroma, also known as intermetatarsal neuroma, is a painful condition that affects the ball of the foot, specifically the area between the third and fourth toes. This condition involves a thickening of the tissue around one of the nerves leading to the toes. The thickening of the tissue can cause sharp, burning pain, numbness, and tingling in the toes and the ball of the foot.
The development of Morton's neuroma is often attributed to repetitive stress or irritation of the nerve, leading to the thickening of the tissue. This can be caused by wearing tight or high-heeled shoes, engaging in high-impact activities such as running or jumping, or having certain foot deformities that put pressure on the nerves.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for Morton's neuroma is crucial for effectively managing and preventing this condition. By gaining insight into the nature of Morton's neuroma, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate discomfort and maintain optimal foot health.
Read more: Possible Causes Of Knee Pain While Cycling
Symptoms of Morton's Neuroma
Morton's neuroma manifests through a range of distressing symptoms that can significantly impact an individual's daily activities and overall well-being. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early detection and prompt intervention. The following are common indicators of Morton's neuroma:
-
Pain and Discomfort: Individuals with Morton's neuroma often experience sharp, shooting pain in the ball of the foot, particularly between the third and fourth toes. This pain may intensify during weight-bearing activities such as walking or running, and can be described as a feeling of stepping on a pebble or a fold in the sock.
-
Numbness and Tingling: A sensation of numbness or tingling in the toes and the ball of the foot is a prevalent symptom of Morton's neuroma. This can lead to a loss of sensation and a feeling of pins and needles in the affected area.
-
Burning Sensation: Many individuals with Morton's neuroma report a burning or stinging sensation in the ball of the foot, which can be exacerbated by wearing tight or constrictive footwear.
-
Feeling of a Lump or Object: Some individuals may perceive a lump or the presence of a foreign object in the ball of the foot, despite no physical obstruction being present. This sensation can be disconcerting and may prompt individuals to frequently check their footwear for any perceived obstructions.
-
Worsening Symptoms: The symptoms of Morton's neuroma often worsen over time, especially if the underlying causes are not addressed. As the condition progresses, the pain and discomfort can become more pronounced, impacting mobility and overall quality of life.
Recognizing these symptoms is pivotal for seeking appropriate medical attention and implementing targeted interventions to alleviate discomfort and prevent the progression of Morton's neuroma. If individuals experience any of these symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan is essential for effectively managing this condition.
Causes of Morton's Neuroma
Morton's neuroma can be attributed to various factors that contribute to the development and exacerbation of this painful foot condition. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for implementing targeted preventive measures and effective management strategies. The following factors are commonly associated with the onset of Morton's neuroma:
-
Footwear: Wearing ill-fitting or constrictive footwear, particularly high heels or narrow-toed shoes, can exert excessive pressure on the forefoot. Prolonged use of such footwear can lead to compression and irritation of the intermetatarsal nerves, contributing to the development of Morton's neuroma.
-
High-Impact Activities: Engaging in high-impact sports or activities that involve repetitive pressure on the forefoot, such as running, basketball, or tennis, can strain the metatarsal bones and surrounding tissues. This repetitive stress can lead to inflammation and thickening of the nerve tissue, resulting in the formation of Morton's neuroma.
-
Foot Deformities: Certain foot deformities, such as bunions, hammertoes, or flat feet, can alter the distribution of weight and pressure on the forefoot. As a result, the nerves in the intermetatarsal spaces may become compressed or irritated, predisposing individuals to the development of Morton's neuroma.
-
Biomechanical Issues: Abnormal foot mechanics, including overpronation or excessive supination, can disrupt the natural alignment of the foot and increase the strain on the metatarsal heads. This biomechanical imbalance can contribute to nerve compression and the subsequent onset of Morton's neuroma.
-
Trauma or Injury: Previous trauma or injury to the foot, such as a sprain or fracture, can lead to structural changes and instability in the forefoot region. These alterations may result in abnormal pressure distribution and nerve irritation, potentially leading to the development of Morton's neuroma.
-
Occupational Factors: Certain occupations that involve prolonged standing or walking on hard surfaces can subject the feet to repetitive mechanical stress. Over time, this chronic stress can contribute to the development of Morton's neuroma, particularly in individuals who are predisposed to foot-related conditions.
Understanding these underlying causes empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle choices and take proactive measures to mitigate the risk of developing Morton's neuroma. By addressing modifiable risk factors, such as footwear selection and biomechanical issues, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing this debilitating foot condition. Additionally, early intervention and targeted preventive strategies can play a pivotal role in preserving foot health and overall well-being.
Diagnosing Morton's Neuroma
Diagnosing Morton's neuroma involves a comprehensive assessment that encompasses a thorough evaluation of the individual's medical history, a detailed physical examination, and, in some cases, diagnostic imaging studies. Healthcare professionals employ a multifaceted approach to accurately diagnose Morton's neuroma and differentiate it from other foot conditions with similar symptoms. The diagnostic process is instrumental in guiding the development of a tailored treatment plan and implementing targeted interventions to alleviate discomfort and restore optimal foot function.
Medical History
The diagnostic journey commences with a detailed review of the individual's medical history, focusing on the onset and progression of symptoms related to foot pain, numbness, and tingling. Healthcare providers inquire about the nature of the discomfort, its triggers, and any factors that exacerbate or alleviate the symptoms. Additionally, individuals are encouraged to provide information about their footwear choices, occupational activities, and participation in sports or high-impact activities, as these factors can offer valuable insights into the potential causes of their foot condition.
Physical Examination
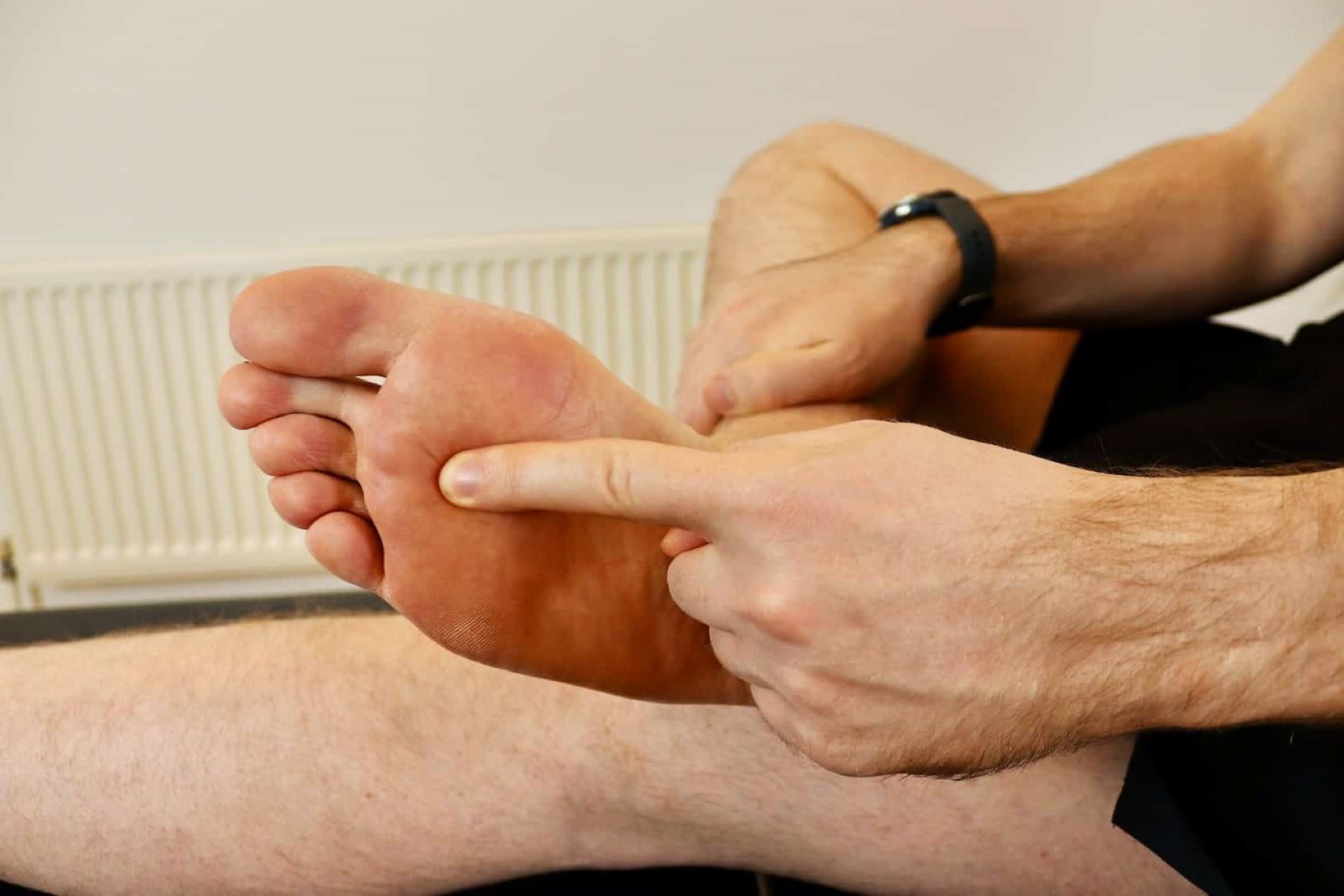
A comprehensive physical examination is pivotal in assessing the foot structure, identifying areas of tenderness or swelling, and eliciting specific signs indicative of Morton's neuroma. Healthcare professionals apply gentle pressure to the forefoot and manipulate the metatarsal heads to reproduce the individual's symptoms. The presence of a Mulder's click, characterized by a palpable click or movement between the metatarsal heads, may be observed during the physical examination, further supporting the diagnosis of Morton's neuroma.
Diagnostic Imaging
In certain cases, diagnostic imaging studies such as X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended to visualize the internal structures of the foot and confirm the presence of Morton's neuroma. X-rays can help assess the alignment of the metatarsal bones and identify any underlying foot deformities, while ultrasound and MRI provide detailed images of the soft tissues and nerves, aiding in the visualization of the neuroma and its precise location within the intermetatarsal spaces.
Differential Diagnosis
Distinguishing Morton's neuroma from other foot conditions with similar symptoms, such as stress fractures, bursitis, or metatarsalgia, is essential during the diagnostic process. Healthcare providers utilize their clinical expertise and the findings from the medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging to rule out alternative diagnoses and ensure an accurate assessment of the individual's foot condition.
Collaborative Approach
The diagnosis of Morton's neuroma often involves a collaborative approach, with podiatrists, orthopedic specialists, and radiologists working together to interpret the clinical findings and imaging studies. This multidisciplinary collaboration enhances the accuracy of the diagnosis and facilitates the development of a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual's specific needs.
By integrating these diagnostic components, healthcare professionals can effectively identify Morton's neuroma, enabling individuals to embark on a targeted treatment journey aimed at alleviating discomfort, restoring foot function, and enhancing overall quality of life. Early and accurate diagnosis forms the cornerstone of proactive management strategies, empowering individuals to take proactive steps towards optimal foot health and well-being.
Treatment Options for Morton's Neuroma
The management of Morton's neuroma encompasses a diverse array of treatment options aimed at alleviating pain, reducing inflammation, and restoring optimal foot function. Healthcare professionals tailor treatment plans to address the unique needs and preferences of individuals, with a focus on mitigating discomfort and enhancing overall foot health. From conservative measures to advanced interventions, the following treatment options are commonly employed in the comprehensive management of Morton's neuroma:
-
Footwear Modification: Encouraging individuals to wear supportive, well-fitted shoes with a wide toe box can alleviate pressure on the forefoot and reduce irritation of the intermetatarsal nerves. Avoiding high heels and narrow-toed footwear is essential to minimize compression on the metatarsal heads and mitigate the symptoms of Morton's neuroma.
-
Orthotic Devices: Custom orthotic inserts or arch supports can optimize foot biomechanics, redistribute pressure, and provide cushioning to the forefoot. These devices help alleviate strain on the metatarsal heads and promote proper foot alignment, thereby reducing the impact on the affected nerve and enhancing overall comfort during weight-bearing activities.
-
Padding and Taping: Healthcare providers may recommend the use of metatarsal pads or toe separators to create space between the metatarsal heads and alleviate compression on the affected nerve. Additionally, taping techniques that support the transverse arch of the foot can provide temporary relief and minimize the exacerbation of symptoms during physical activities.
-
Footwear Modifications: In cases where conservative measures do not provide adequate relief, corticosteroid injections may be considered to alleviate pain and inflammation associated with Morton's neuroma. These injections are administered under the guidance of a healthcare professional and aim to reduce nerve irritation and provide temporary relief from discomfort.
-
Physical Therapy: Engaging in targeted physical therapy exercises can strengthen the intrinsic muscles of the foot, improve foot mechanics, and enhance flexibility. Physical therapists design personalized exercise regimens to address muscle imbalances, optimize gait patterns, and alleviate pressure on the forefoot, contributing to long-term symptom management and functional improvement.
-
Surgical Intervention: In instances where conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms, surgical intervention may be recommended to address Morton's neuroma. Surgical procedures such as neurectomy, where the affected nerve is removed or decompressed, can provide lasting relief for individuals with persistent or severe symptoms. Healthcare providers carefully evaluate the individual's condition and discuss the potential risks and benefits of surgical intervention to ensure informed decision-making.
-
Regenerative Medicine: Emerging regenerative therapies, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections or stem cell treatments, are being explored as potential options for managing Morton's neuroma. These innovative approaches aim to promote tissue healing, reduce inflammation, and modulate pain perception, offering promising avenues for non-invasive intervention and symptom relief.
By integrating these diverse treatment options, healthcare professionals strive to empower individuals with Morton's neuroma to embark on a personalized treatment journey tailored to their unique needs and preferences. The comprehensive approach to managing Morton's neuroma encompasses a continuum of care, from conservative measures to advanced interventions, with the overarching goal of enhancing foot comfort, function, and overall quality of life.
Preventing Morton's Neuroma
Preventing Morton's neuroma involves proactive measures aimed at mitigating the risk factors associated with this debilitating foot condition. By adopting a multifaceted approach that encompasses lifestyle modifications, proper footwear selection, and targeted preventive strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing Morton's neuroma and preserve optimal foot health.
Footwear Selection
Choosing appropriate footwear is paramount in preventing Morton's neuroma. Opting for shoes with a wide toe box and ample cushioning can alleviate pressure on the forefoot and minimize compression of the intermetatarsal nerves. Additionally, avoiding high heels and narrow-toed shoes is essential to mitigate the risk of nerve irritation and the development of Morton's neuroma. By prioritizing comfort and proper fit, individuals can safeguard their foot health and reduce the likelihood of experiencing foot-related conditions.
Orthotic Support
Utilizing custom orthotic inserts or arch supports can optimize foot biomechanics, redistribute pressure, and provide cushioning to the forefoot. These supportive devices aid in maintaining proper foot alignment, reducing strain on the metatarsal heads, and mitigating the risk of developing Morton's neuroma. By integrating orthotic support into footwear, individuals can enhance foot comfort and minimize the impact of repetitive mechanical stress on the forefoot.
Read more: 4 Common Causes Of Knee Pain After Running
Biomechanical Assessment
Undergoing a comprehensive biomechanical assessment by a qualified healthcare professional can identify any foot abnormalities or gait irregularities that may predispose individuals to Morton's neuroma. Addressing biomechanical issues, such as overpronation or excessive supination, through targeted interventions and corrective measures can mitigate the strain on the metatarsal heads and reduce the likelihood of nerve compression. By proactively addressing biomechanical imbalances, individuals can optimize foot function and minimize the risk of developing Morton's neuroma.
Gradual Training Progression
For individuals engaged in high-impact activities such as running or sports that involve repetitive pressure on the forefoot, adopting a gradual training progression is crucial in preventing Morton's neuroma. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activities allows the foot structures to adapt and reduces the risk of overloading the metatarsal heads. By implementing a structured training regimen and incorporating adequate rest periods, individuals can minimize the likelihood of developing Morton's neuroma due to excessive mechanical stress.
Regular Foot Care
Prioritizing regular foot care, including proper hygiene, nail trimming, and monitoring for any signs of discomfort or abnormalities, is essential in preventing Morton's neuroma. By maintaining foot health and promptly addressing any emerging issues, individuals can mitigate the impact of external factors that may contribute to the development of foot-related conditions. Additionally, seeking professional guidance for foot care and incorporating preventive measures into daily routines can contribute to long-term foot health and overall well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making conscious lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy body weight, engaging in low-impact exercises, and incorporating foot-friendly practices into daily activities, can significantly reduce the risk of Morton's neuroma. By prioritizing overall health and wellness, individuals can minimize the burden on the forefoot and mitigate the potential factors that contribute to the onset of this painful foot condition.
By integrating these preventive strategies into daily routines and lifestyle choices, individuals can proactively mitigate the risk of developing Morton's neuroma and preserve optimal foot health. Empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools to prevent this condition is instrumental in fostering a proactive approach to foot care and enhancing overall well-being.