Home>Health & Nutrition>Injury Prevention>Understanding The Causes Of Tight Hip Flexors And Effective Ways To Loosen Them


Injury Prevention
Understanding The Causes Of Tight Hip Flexors And Effective Ways To Loosen Them
Published: March 1, 2024
Learn the causes of tight hip flexors and effective ways to loosen them for injury prevention. Improve flexibility and reduce discomfort with these tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Common Causes of Tight Hip Flexors
Tight hip flexors are a common issue that can result from various factors, including sedentary lifestyles, improper posture, and overuse. Understanding the causes of tight hip flexors is crucial for effectively addressing and preventing this discomforting condition. Here are the common causes of tight hip flexors:
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: Prolonged periods of sitting, whether at a desk, in front of a computer, or during extended commutes, can lead to tight hip flexors. When the hip flexors remain in a shortened position for an extended period, they can become tight and stiff, limiting their range of motion.
-
Lack of Physical Activity: Insufficient physical activity and exercise can contribute to the tightening of hip flexor muscles. When the body is not engaged in regular movement, the hip flexors may become weak and prone to tightening.
-
Poor Posture: Slouching or sitting with improper posture can place undue stress on the hip flexors, leading to tightness over time. This is particularly common in individuals who spend long hours working at a desk or engaging in activities that encourage poor posture.
-
Overuse and Repetitive Movements: Engaging in activities that repeatedly engage the hip flexor muscles, such as cycling, running, or excessive stair climbing, can lead to tightness and overuse of these muscles.
-
Muscle Imbalance: Imbalances between the hip flexor muscles and their opposing muscle groups, such as the glutes and hamstrings, can contribute to tightness in the hip flexors. Weakness in the opposing muscle groups can lead to compensatory tightening of the hip flexors.
-
Inadequate Warm-Up or Cool-Down: Failing to properly warm up before physical activity or neglecting to cool down after exercise can contribute to tight hip flexors. Without adequate preparation and recovery, the hip flexors may become tight and prone to discomfort.
Understanding these common causes of tight hip flexors is essential for taking proactive measures to address and prevent this issue. By incorporating targeted exercises, lifestyle adjustments, and mindful movement practices, individuals can effectively alleviate tightness in the hip flexors and promote overall musculoskeletal health.
The Impact of Tight Hip Flexors on the Body
Tight hip flexors can exert a far-reaching impact on the body, affecting various aspects of musculoskeletal health and overall well-being. These effects extend beyond localized discomfort, potentially influencing posture, movement patterns, and even organ function. Understanding the comprehensive impact of tight hip flexors is crucial for recognizing the significance of addressing this issue and implementing effective preventive measures.
Postural Alignment and Stability
Tight hip flexors can disrupt the body's natural postural alignment, leading to an anterior pelvic tilt. This misalignment can cause the pelvis to tilt forward, placing excessive strain on the lower back and altering the curvature of the spine. As a result, individuals with tight hip flexors may experience lower back pain, reduced stability, and compromised posture, impacting their overall physical well-being.
Movement Patterns and Range of Motion
The flexibility and mobility of the hip flexors play a pivotal role in facilitating smooth and unrestricted movement. When these muscles become tight, they can restrict the range of motion in the hips, affecting activities such as walking, running, and bending. Consequently, individuals may experience diminished agility, compromised athletic performance, and an increased risk of injury due to restricted movement patterns.
Core Strength and Stability
The hip flexors are intricately connected to the core muscles, contributing to overall stability and strength. Tight hip flexors can disrupt the balance between the muscles of the core and the pelvis, potentially compromising core stability. This imbalance may lead to weakened core muscles, reduced functional strength, and an increased susceptibility to back injuries and postural imbalances.
Organ Function and Circulation
The positioning of the hip flexors in the body can impact the functioning of vital organs and circulatory pathways. Tight hip flexors can exert pressure on the abdomen, potentially affecting digestion and organ function. Furthermore, this tightness can impede blood flow to the lower body, contributing to discomfort and reduced circulation in the pelvic region.
Emotional Well-being and Stress
The physical discomfort associated with tight hip flexors can also influence emotional well-being. Chronic tightness in this area can contribute to feelings of stress, tension, and discomfort, potentially impacting an individual's overall mental and emotional state. Addressing tight hip flexors can thus contribute to a sense of physical ease and emotional well-being.
Understanding the multifaceted impact of tight hip flexors underscores the importance of proactive measures to address and prevent this issue. By incorporating targeted stretching exercises, strengthening routines, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can mitigate the adverse effects of tight hip flexors, promoting optimal musculoskeletal health and overall well-being.
Symptoms of Tight Hip Flexors
Tight hip flexors can manifest a range of discomforting symptoms that extend beyond localized muscle tightness. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for identifying and addressing the underlying issue effectively. Here are the key symptoms associated with tight hip flexors:
-
Lower Back Discomfort: Tight hip flexors can contribute to lower back pain and discomfort, stemming from the altered pelvic position and increased strain on the lumbar spine. Individuals with tight hip flexors may experience persistent or intermittent lower back pain, particularly after prolonged periods of sitting or engaging in physical activities.
-
Hip and Groin Discomfort: Tightness in the hip flexor muscles can lead to discomfort and stiffness in the hips and groin area. This may manifest as a sensation of tightness or restricted movement when attempting to flex or extend the hips, impacting activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or performing exercises that involve hip mobility.
-
Limited Range of Motion: Individuals with tight hip flexors may notice a reduced range of motion in the hips, affecting their ability to perform activities that require hip flexibility, such as lunging, squatting, or kicking. This limitation in mobility can impede functional movements and compromise overall physical performance.
-
Postural Changes: Tight hip flexors can contribute to postural imbalances, leading to an anterior pelvic tilt and an exaggerated curvature of the lower back. This altered posture may result in a protruding abdomen and a flattened lumbar spine, affecting overall postural alignment and stability.
-
Discomfort During Physical Activity: Engaging in physical activities that involve hip extension, such as running, cycling, or performing lower body exercises, may exacerbate the discomfort associated with tight hip flexors. Individuals may experience a sensation of tightness or discomfort in the front of the hips during these activities.
-
Disrupted Gait Patterns: Tight hip flexors can influence gait mechanics, potentially leading to an altered walking pattern characterized by shortened strides, reduced hip extension, and increased pelvic tilt. These changes in gait can contribute to inefficient movement patterns and an increased risk of lower extremity injuries.
-
Muscle Stiffness and Tension: Individuals with tight hip flexors may experience a persistent sensation of muscle stiffness and tension in the front of the hips, potentially radiating down into the thighs. This discomfort can be particularly noticeable after prolonged periods of inactivity or when transitioning from sitting to standing.
Recognizing these symptoms of tight hip flexors is essential for implementing targeted interventions to alleviate discomfort and restore optimal hip mobility. By incorporating stretching exercises, strengthening routines, and postural awareness, individuals can effectively address tight hip flexors and promote overall musculoskeletal well-being.
Effective Ways to Loosen Tight Hip Flexors
Loosening tight hip flexors is essential for alleviating discomfort, improving mobility, and promoting overall musculoskeletal health. Incorporating targeted strategies to address this issue can effectively restore flexibility and function to the hip flexor muscles. Here are several effective ways to loosen tight hip flexors:
Read more: 3 Essential Hip Flexor Exercises For Runners
1. Incorporate Dynamic Stretching:
Dynamic stretching exercises, such as leg swings, hip circles, and walking lunges, can help to actively mobilize and lengthen the hip flexor muscles. These dynamic movements promote increased blood flow and flexibility in the hip flexors, contributing to a gradual reduction in tightness and stiffness.
2. Perform Static Hip Flexor Stretches:
Engaging in static stretches that specifically target the hip flexors, such as the kneeling hip flexor stretch or the standing quad stretch, can effectively alleviate tightness in this area. Holding these stretches for 20-30 seconds on each side can help to gradually release tension and improve the flexibility of the hip flexor muscles.
3. Utilize Foam Rolling Techniques:
Foam rolling the hip flexor muscles can provide targeted myofascial release, helping to alleviate tightness and promote relaxation in the surrounding tissues. By gently rolling back and forth over the front of the hips, individuals can reduce muscular tension and enhance the suppleness of the hip flexors.
4. Engage in Psoas Muscle Release:
The psoas muscle, a deep-seated hip flexor, can significantly contribute to tightness in the hip flexor region. Utilizing techniques such as self-massage with a massage ball or foam roller can help release tension in the psoas muscle, contributing to improved hip flexor flexibility.
Read more: All You Need To Know About Hip Flexor Strain
5. Practice Hip Flexor Strengthening Exercises:
Incorporating targeted strengthening exercises for the hip flexors, such as leg raises, mountain climbers, and bicycle crunches, can help to enhance the strength and stability of these muscles. Strengthening the hip flexors in conjunction with stretching can contribute to improved overall function and reduced tightness.
6. Implement Postural Awareness:
Maintaining proper posture throughout daily activities can help prevent the exacerbation of tight hip flexors. Focusing on aligning the pelvis and maintaining a neutral spine can reduce the likelihood of excessive tightening in the hip flexor muscles.
7. Consider Professional Intervention:
Seeking guidance from a physical therapist or a qualified healthcare professional can provide personalized strategies for addressing tight hip flexors. These professionals can offer tailored exercises, manual therapy techniques, and ergonomic recommendations to effectively alleviate tightness and promote optimal hip mobility.
Incorporating these effective strategies into a comprehensive approach to addressing tight hip flexors can yield significant improvements in flexibility, comfort, and overall musculoskeletal well-being. By consistently implementing these methods, individuals can effectively loosen tight hip flexors and experience enhanced mobility and comfort in daily activities.
Stretching Exercises for Hip Flexors
Stretching exercises play a pivotal role in alleviating tightness and promoting flexibility in the hip flexor muscles. Incorporating targeted stretches can effectively release tension and improve the range of motion in this crucial area, contributing to enhanced mobility and reduced discomfort. Here are several stretching exercises specifically designed to target the hip flexors:
1. Kneeling Hip Flexor Stretch:
Begin by assuming a kneeling position on a padded surface. Step one foot forward, ensuring that the knee is positioned directly above the ankle. Gently shift your weight forward, maintaining an upright posture, until you feel a comfortable stretch in the front of the hip and thigh of the back leg. Hold this position for 20-30 seconds, then switch to stretch the opposite hip flexor.
2. Standing Quad Stretch:
Stand upright with feet hip-width apart. Lift one foot behind you and grasp the ankle with the corresponding hand. Gently pull the foot towards the glutes, feeling a stretch in the front of the thigh and hip. Hold this position for 20-30 seconds, then switch to stretch the opposite leg.
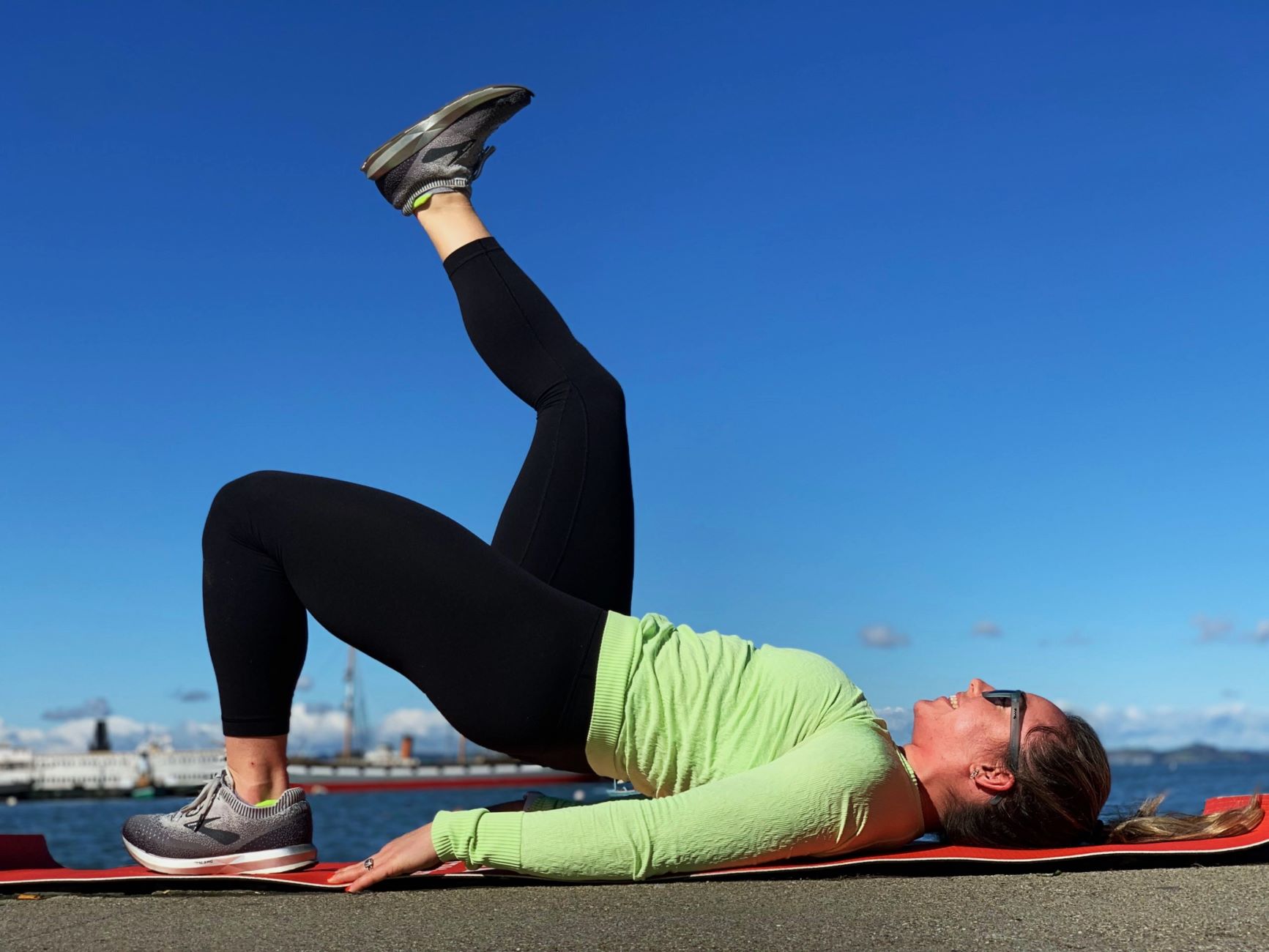
3. Supine Hip Flexor Stretch:
Lie on your back with both legs extended. Bend one knee and bring it towards the chest. Grasp the back of the thigh with both hands and gently pull the knee towards the chest, feeling a stretch in the front of the hip. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then switch to stretch the opposite hip flexor.
4. Pigeon Pose:
From a tabletop position, slide one knee forward towards the same-side wrist, allowing the shin to rest on the floor at a diagonal angle. Extend the opposite leg behind you, ensuring the hips are squared. Slowly lower your upper body towards the floor, feeling a deep stretch in the hip of the front leg. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then switch to stretch the opposite hip flexor.
5. Standing Hip Flexor Stretch:
Stand with feet hip-width apart. Take a step back with one foot and bend the front knee, ensuring it remains aligned with the ankle. Tilt the pelvis slightly forward, feeling a stretch in the hip flexor of the back leg. Hold for 20-30 seconds, then switch to stretch the opposite side.
Incorporating these stretching exercises into a regular routine can effectively alleviate tightness and promote flexibility in the hip flexor muscles. Consistent practice of these stretches, combined with proper warm-up and cool-down techniques, can contribute to improved hip mobility and reduced discomfort associated with tight hip flexors.
Strengthening Exercises for Hip Flexors
Strengthening the hip flexor muscles is essential for promoting stability, mobility, and overall musculoskeletal function. Incorporating targeted exercises to enhance the strength of the hip flexors can contribute to improved posture, reduced risk of injury, and enhanced performance in various physical activities. Here are several effective strengthening exercises specifically designed to target the hip flexors:
-
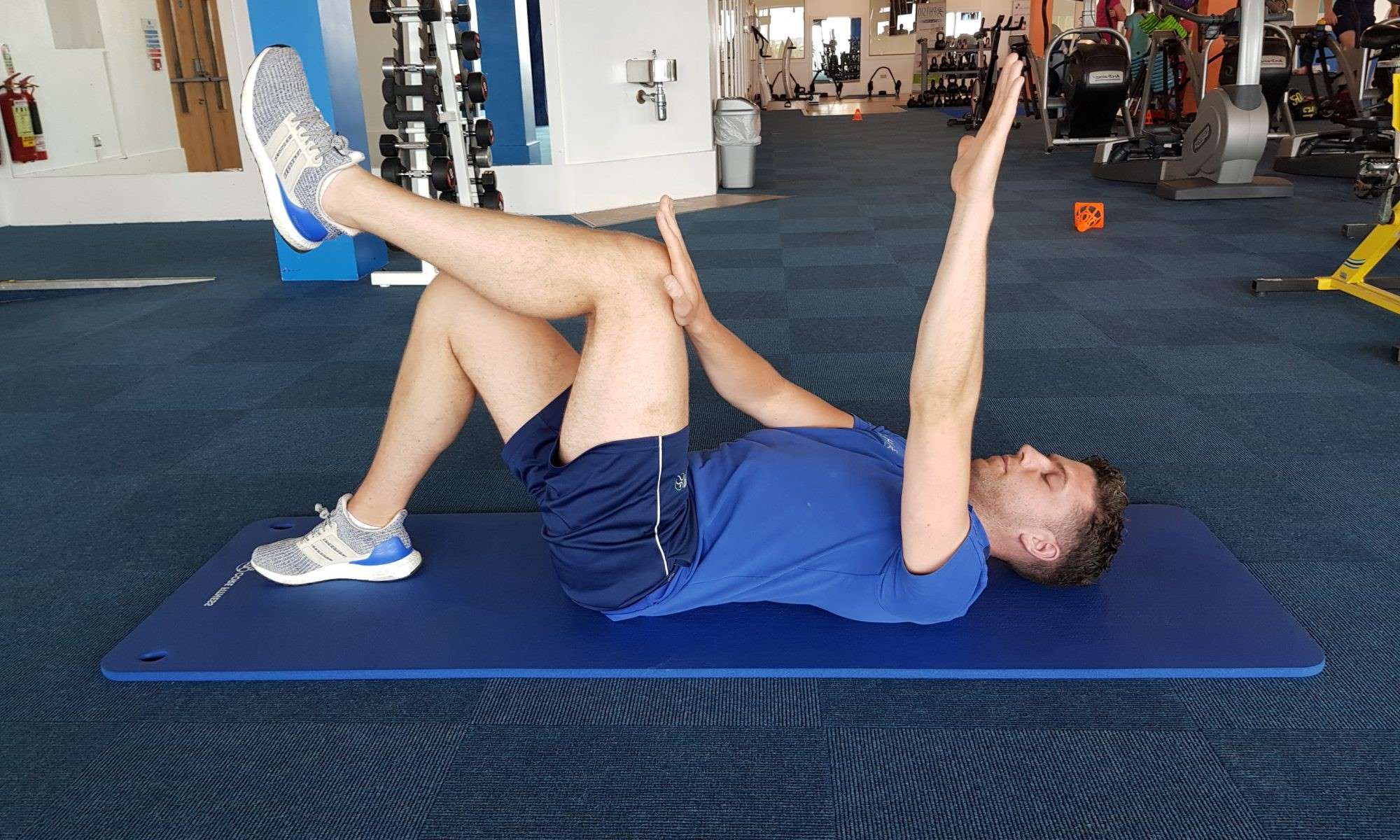
Leg Raises:
- Lie on your back with legs extended.
- Lift one leg off the ground, keeping it straight, and hold for a few seconds.
- Slowly lower the leg back to the starting position.
- Perform 10-15 repetitions on each leg, gradually increasing the number as strength improves.
-
Mountain Climbers:
- Begin in a plank position, with the arms extended and the body forming a straight line.
- Alternately bring each knee towards the chest in a running motion, engaging the hip flexors.
- Perform this exercise for 30-60 seconds, maintaining a steady pace and focusing on controlled movements.
-
Bicycle Crunches:
- Lie on your back with hands behind your head and legs lifted off the ground.
- Bring one knee towards the chest while simultaneously twisting the torso to bring the opposite elbow towards the knee.
- Alternate between sides in a pedaling motion, engaging the hip flexors and abdominal muscles.
- Perform 10-15 repetitions on each side, focusing on controlled and deliberate movements.
-
Standing Knee Raises:
- Stand upright with feet hip-width apart.
- Lift one knee towards the chest, engaging the hip flexors, and hold for a few seconds.
- Slowly lower the leg back to the ground and repeat on the opposite side.
- Perform 10-15 repetitions on each leg, gradually increasing the number as strength improves.
-
Plank with Leg Lifts:
- Begin in a forearm plank position, with the body forming a straight line from head to heels.
- Lift one leg off the ground, engaging the hip flexors and maintaining a stable plank position.
- Hold the leg lifted for a few seconds before lowering it back to the ground.
- Alternate between legs, performing 10-15 repetitions on each side.
Incorporating these strengthening exercises into a regular workout routine can effectively target the hip flexor muscles, promoting enhanced strength and stability in this crucial area. It is important to perform these exercises with proper form and control to maximize their effectiveness and minimize the risk of strain or injury. Additionally, gradually increasing the intensity and resistance of these exercises as strength improves can further enhance the benefits of hip flexor strengthening.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Tight Hip Flexors
In addition to targeted exercises and stretches, making lifestyle adjustments can play a pivotal role in preventing the development of tight hip flexors. By incorporating mindful movement practices, ergonomic modifications, and postural awareness into daily routines, individuals can proactively mitigate the risk of tightness in the hip flexor muscles. Here are several lifestyle changes that can effectively contribute to the prevention of tight hip flexors:
-
Regular Movement Breaks: Incorporating regular movement breaks throughout the day can help counteract the effects of prolonged sitting and sedentary behavior. Taking short walks, performing gentle stretches, or engaging in brief standing activities can prevent the hip flexors from remaining in a consistently shortened position, promoting flexibility and circulation in this crucial area.
-
Ergonomic Workstation Setup: Ensuring an ergonomic workstation setup can significantly reduce the risk of developing tight hip flexors due to prolonged sitting. Adjusting the height and positioning of the chair, desk, and computer monitor to promote proper posture and alignment can alleviate undue stress on the hip flexors, contributing to improved musculoskeletal health.
-
Hip-Opening Activities: Participating in activities that promote hip opening, such as yoga, Pilates, or dance, can effectively counteract the tightening effects of sedentary lifestyles. These activities emphasize movements that engage and stretch the hip flexors, contributing to improved flexibility and mobility in this area.
-
Mindful Sitting Practices: Practicing mindful sitting techniques, such as maintaining a neutral pelvis, avoiding prolonged slouching, and utilizing supportive seating, can prevent excessive tightening of the hip flexors. Mindful sitting promotes proper alignment and reduces the strain on the hip flexor muscles, contributing to improved comfort and mobility.
-
Active Lifestyle Choices: Embracing an active lifestyle that includes a variety of physical activities, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can prevent the development of tight hip flexors. Engaging in diverse movements that promote hip extension and flexibility can effectively counteract the effects of prolonged sitting and sedentary behavior.
-
Postural Awareness: Cultivating postural awareness in daily activities, such as standing, walking, and lifting, can prevent the exacerbation of tight hip flexors. Focusing on maintaining a neutral pelvis, avoiding excessive anterior pelvic tilt, and engaging the core muscles can promote optimal alignment and reduce the strain on the hip flexors.
By integrating these lifestyle changes into daily routines, individuals can effectively prevent the development of tight hip flexors, promoting enhanced flexibility, comfort, and overall musculoskeletal well-being. These proactive measures, combined with targeted exercises and stretches, can contribute to optimal hip mobility and reduced risk of discomfort associated with tight hip flexors.