Home>Health & Nutrition>Injury Prevention>Effective Exercises And Treatment For Plantar Fasciitis

Injury Prevention
Effective Exercises And Treatment For Plantar Fasciitis
Published: February 26, 2024
Discover effective exercises and treatments for plantar fasciitis to prevent injury and promote foot health. Learn how to manage and alleviate symptoms with expert guidance.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
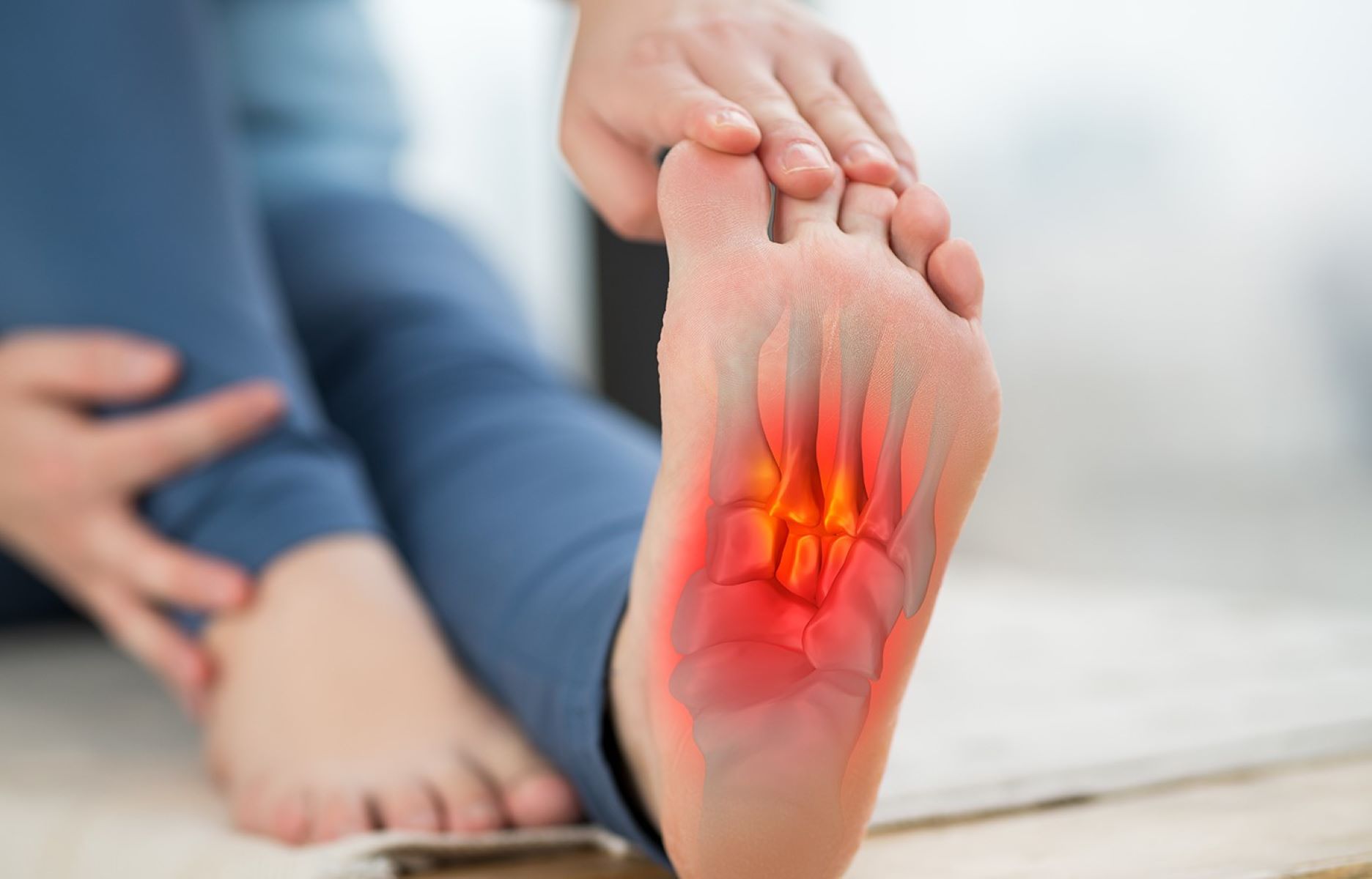
Understanding Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition that causes pain in the heel and the bottom of the foot. It occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes, becomes inflamed or irritated. This can result in stabbing pain that is usually most severe with the first steps of the day.
The plantar fascia plays a crucial role in supporting the arch of the foot and in absorbing shock when walking or running. When this band of tissue is strained or overused, small tears can develop, leading to inflammation and pain.
Individuals who are overweight, have high arches or flat feet, or engage in activities that place excessive stress on the feet are at a higher risk of developing plantar fasciitis. Additionally, wearing unsupportive footwear or suddenly increasing physical activity can also contribute to the development of this condition.
Understanding the symptoms of plantar fasciitis is essential for early detection and treatment. The most common symptoms include sharp pain in the heel or along the arch of the foot, especially after long periods of rest or physical activity. The pain may also worsen after standing for extended periods or climbing stairs.
Plantar fasciitis can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, making it difficult to engage in regular activities and exercise. Therefore, seeking prompt medical attention and adopting preventive measures are crucial steps in managing this condition effectively.
By gaining a deeper understanding of plantar fasciitis, individuals can take proactive measures to alleviate discomfort and prevent the condition from worsening. This includes incorporating targeted exercises, seeking appropriate treatment, and implementing preventive strategies to promote foot health and overall well-being.
Read more: The Importance Of Jump Squats For Runners
Common Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis can develop due to a variety of factors, many of which involve repetitive stress and overuse of the foot. Understanding the common causes of this condition is essential for identifying potential risk factors and taking proactive measures to prevent its onset. Here are the primary factors that contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis:
-
Overuse and High-Impact Activities: Engaging in high-impact sports and activities that involve prolonged standing or walking can strain the plantar fascia, leading to micro-tears and inflammation. Runners, dancers, and individuals who spend long hours on their feet are particularly susceptible to this type of injury.
-
Improper Footwear: Wearing unsupportive or ill-fitting footwear can exacerbate the risk of developing plantar fasciitis. Shoes with inadequate arch support, insufficient cushioning, or poor shock absorption can place excessive strain on the plantar fascia, contributing to its inflammation and subsequent pain.
-
Biomechanical Factors: Certain foot structures and biomechanical abnormalities can increase the likelihood of developing plantar fasciitis. Flat feet, high arches, and abnormal walking patterns can alter the distribution of weight and impact forces on the feet, leading to heightened stress on the plantar fascia.
-
Obesity and Weight Distribution: Excess body weight places additional strain on the plantar fascia, especially during weight-bearing activities. The increased pressure on the feet can contribute to the development of micro-tears in the plantar fascia, resulting in inflammation and heel pain.
-
Tightness and Muscle Imbalance: Tight calf muscles and Achilles tendons, as well as weak or imbalanced foot and leg muscles, can alter the mechanics of the foot and increase the risk of plantar fasciitis. These muscular imbalances can lead to abnormal foot pronation or supination, placing undue stress on the plantar fascia.
-
Sudden Changes in Activity Level: Abruptly increasing the intensity, duration, or frequency of physical activities, such as running or exercising, can strain the plantar fascia and lead to the development of plantar fasciitis. Gradual progression and proper conditioning are essential in preventing overuse injuries.
By recognizing these common causes of plantar fasciitis, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate risk factors and promote foot health. Implementing appropriate footwear, incorporating targeted stretching and strengthening exercises, and maintaining a healthy body weight are essential strategies for preventing the onset of plantar fasciitis and minimizing the risk of recurring symptoms.
Effective Exercises for Plantar Fasciitis
Incorporating targeted exercises into a comprehensive treatment plan is crucial for managing plantar fasciitis and promoting foot health. These exercises are designed to stretch and strengthen the muscles and connective tissues in the foot and lower leg, alleviating pain and enhancing flexibility. By engaging in a consistent exercise routine, individuals can effectively reduce discomfort, improve mobility, and prevent the recurrence of plantar fasciitis symptoms.
1. Calf Stretches
Performing calf stretches helps alleviate tension in the Achilles tendon and calf muscles, which can contribute to plantar fasciitis. To execute this exercise, stand facing a wall with one foot forward and the other foot positioned behind. Keep the back knee straight and the heel flat on the ground, while gently leaning forward until a stretch is felt in the calf of the back leg. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each leg.
2. Plantar Fascia Stretch
The plantar fascia stretch targets the band of tissue along the bottom of the foot, promoting flexibility and reducing discomfort. Sit on a chair and cross one foot over the opposite knee. Using one hand, gently pull back the toes of the crossed foot, stretching the arch of the foot and the plantar fascia. Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each foot.
3. Towel Stretch
The towel stretch is an effective way to stretch the plantar fascia and the muscles of the calf. Sit on the floor with both legs extended in front of you. Loop a towel around the ball of one foot and gently pull the towel towards you, keeping the knee straight. Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each foot.
4. Toe Curls
Toe curls help strengthen the muscles of the foot, enhancing stability and support. While seated, place a small towel on the floor and use the toes to scrunch the towel towards you. Repeat this movement for 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions on each foot.
5. Ankle Flexion and Extension
Ankle flexion and extension exercises promote mobility and strength in the ankle joint, aiding in the rehabilitation of plantar fasciitis. Sit on a chair with the feet flat on the ground. Slowly point the toes away from the body and then pull them back towards you, flexing and extending the ankle. Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions for each foot.
Incorporating these exercises into a daily routine can significantly contribute to the management and alleviation of plantar fasciitis symptoms. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a physical therapist before initiating any new exercise regimen, especially if experiencing severe or persistent foot pain. By combining targeted exercises with appropriate treatment modalities, individuals can effectively address plantar fasciitis and enhance their overall foot health and well-being.
Treatment Options for Plantar Fasciitis
Effective treatment for plantar fasciitis aims to alleviate pain, promote healing, and prevent the recurrence of symptoms. By implementing a comprehensive approach that combines conservative therapies, advanced modalities, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can effectively manage this condition and enhance their overall foot health. Here are the primary treatment options for plantar fasciitis:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the affected foot and modifying activities that exacerbate pain are fundamental components of plantar fasciitis treatment. Minimizing weight-bearing activities and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or walking can alleviate strain on the plantar fascia, allowing the tissues to heal and recover.
2. Ice Therapy
Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with plantar fasciitis. Cold therapy can be administered by placing an ice pack or a frozen water bottle under the heel for 15-20 minutes several times a day, particularly after engaging in physical activities.
3. Orthotic Devices
Utilizing orthotic devices, such as supportive shoe inserts or custom-made orthotics, can provide essential arch support and cushioning, reducing stress on the plantar fascia. These devices help distribute pressure evenly across the foot, promoting proper alignment and mitigating discomfort during weight-bearing activities.
4. Stretching and Physical Therapy
Engaging in targeted stretching exercises and physical therapy sessions can enhance flexibility, strengthen the muscles of the foot and lower leg, and improve overall biomechanics. Physical therapists can provide personalized treatment plans that include manual therapy, ultrasound, and specialized exercises to address plantar fasciitis effectively.
5. Footwear Modifications
Wearing supportive and well-cushioned footwear with adequate arch support is crucial for individuals with plantar fasciitis. Shoes that provide shock absorption, stability, and proper heel cushioning can reduce strain on the plantar fascia and promote a more comfortable gait.
6. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with plantar fasciitis. However, it is essential to use these medications as directed and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of use.
7. Corticosteroid Injections
In cases of persistent or severe pain, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide targeted relief from inflammation and discomfort. These injections are administered directly into the affected area, offering temporary relief and facilitating the effectiveness of other conservative treatments.
8. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT)
ESWT is a non-invasive treatment modality that utilizes shock waves to stimulate healing and reduce pain associated with plantar fasciitis. This advanced therapy promotes tissue regeneration and can be particularly beneficial for individuals who have not responded to traditional conservative treatments.
9. Night Splints
Wearing night splints can help alleviate morning pain and stiffness by maintaining a gentle stretch on the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon while sleeping. These devices prevent the tissues from tightening during rest, promoting improved mobility and reduced discomfort upon waking.
10. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the individual's blood into the affected area, promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation. This regenerative treatment option can accelerate the healing process and provide long-term relief from plantar fasciitis symptoms.
By integrating these treatment options into a comprehensive care plan, individuals can effectively address plantar fasciitis and improve their overall foot health. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on the severity of symptoms, individual needs, and medical history. Additionally, adopting preventive measures, such as maintaining a healthy weight, wearing appropriate footwear, and engaging in regular foot care, can contribute to long-term management and the prevention of recurrent plantar fasciitis symptoms.
Prevention Tips for Plantar Fasciitis
Preventing plantar fasciitis involves adopting proactive measures to reduce the risk of developing this painful foot condition. By implementing practical strategies and lifestyle modifications, individuals can safeguard their foot health and minimize the likelihood of experiencing plantar fasciitis symptoms. Here are essential prevention tips to promote overall foot well-being:
-
Proper Footwear: Wearing supportive footwear with adequate arch support, cushioning, and shock absorption is crucial for preventing plantar fasciitis. Choose shoes that provide stability and comfort, especially during high-impact activities or prolonged periods of standing.
-
Gradual Progression: When initiating a new exercise regimen or increasing physical activity, it is essential to progress gradually to allow the body to adapt and minimize the risk of overuse injuries. Gradual progression helps prevent excessive strain on the plantar fascia and reduces the likelihood of developing micro-tears.
-
Stretching Routine: Incorporating regular stretching exercises for the calf muscles, Achilles tendon, and plantar fascia can enhance flexibility and reduce tension in the lower leg and foot. Prior to engaging in physical activities, warming up with dynamic stretches can prepare the muscles and connective tissues for movement, reducing the risk of strain.
-
Maintain Healthy Body Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate excessive pressure on the feet and lower extremities, reducing the risk of developing plantar fasciitis. By adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can manage their weight effectively and promote overall foot health.
-
Foot Care Awareness: Practicing good foot care, including regular inspection of the feet for any signs of discomfort, redness, or swelling, can aid in early detection and prompt management of potential foot conditions. Additionally, keeping the feet clean, dry, and well-moisturized can contribute to overall foot health.
-
Cross-Training and Variation: Incorporating cross-training activities and varying the types of physical exercises can prevent overuse injuries and reduce repetitive stress on the feet. By diversifying workout routines and engaging in low-impact activities, individuals can promote overall musculoskeletal health and minimize the risk of plantar fasciitis.
-
Orthotic Support: Utilizing orthotic devices, such as shoe inserts or custom orthotics, can provide essential support and alignment for the feet, reducing the strain on the plantar fascia. These supportive devices can help distribute pressure evenly and promote proper foot mechanics during weight-bearing activities.
-
Professional Guidance: Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional, such as a podiatrist or physical therapist, can provide personalized recommendations for foot care, footwear selection, and exercise programs. Professional guidance can help individuals make informed decisions to prevent the onset of plantar fasciitis and promote overall foot health.
By incorporating these preventive measures into daily routines and lifestyle habits, individuals can effectively reduce the risk of developing plantar fasciitis and maintain optimal foot health. Proactive foot care, appropriate footwear selection, and a balanced approach to physical activity are essential components of preventing plantar fasciitis and promoting overall well-being.

