Home>Health & Nutrition>Potential Negative Effects Of Excessive Coffee Consumption On Arthritis And Obesity Risk


Health & Nutrition
Potential Negative Effects Of Excessive Coffee Consumption On Arthritis And Obesity Risk
Published: February 23, 2024
Learn about the potential negative effects of excessive coffee consumption on arthritis and obesity risk. Explore the impact on health and nutrition.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Coffee is one of the most beloved beverages worldwide, cherished for its rich aroma and invigorating effects. However, while moderate coffee consumption has been associated with certain health benefits, excessive intake may pose risks, particularly concerning arthritis and obesity. Understanding the potential negative effects of consuming too much coffee on these health conditions is crucial for individuals seeking to maintain a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
In this article, we will delve into the intricate relationship between excessive coffee consumption and the heightened risk of arthritis and obesity. By exploring the scientific evidence and insights from health experts, we aim to shed light on the potential impact of excessive coffee intake on these health concerns. Furthermore, we will provide practical recommendations for managing coffee consumption, especially for individuals at risk of developing arthritis and obesity.
As we embark on this exploration, it's important to approach the topic with an open mind, recognizing that the effects of coffee consumption can vary among individuals. By gaining a deeper understanding of the potential negative implications of excessive coffee intake, we can make informed decisions about our dietary habits and strive for a healthier and more balanced lifestyle.
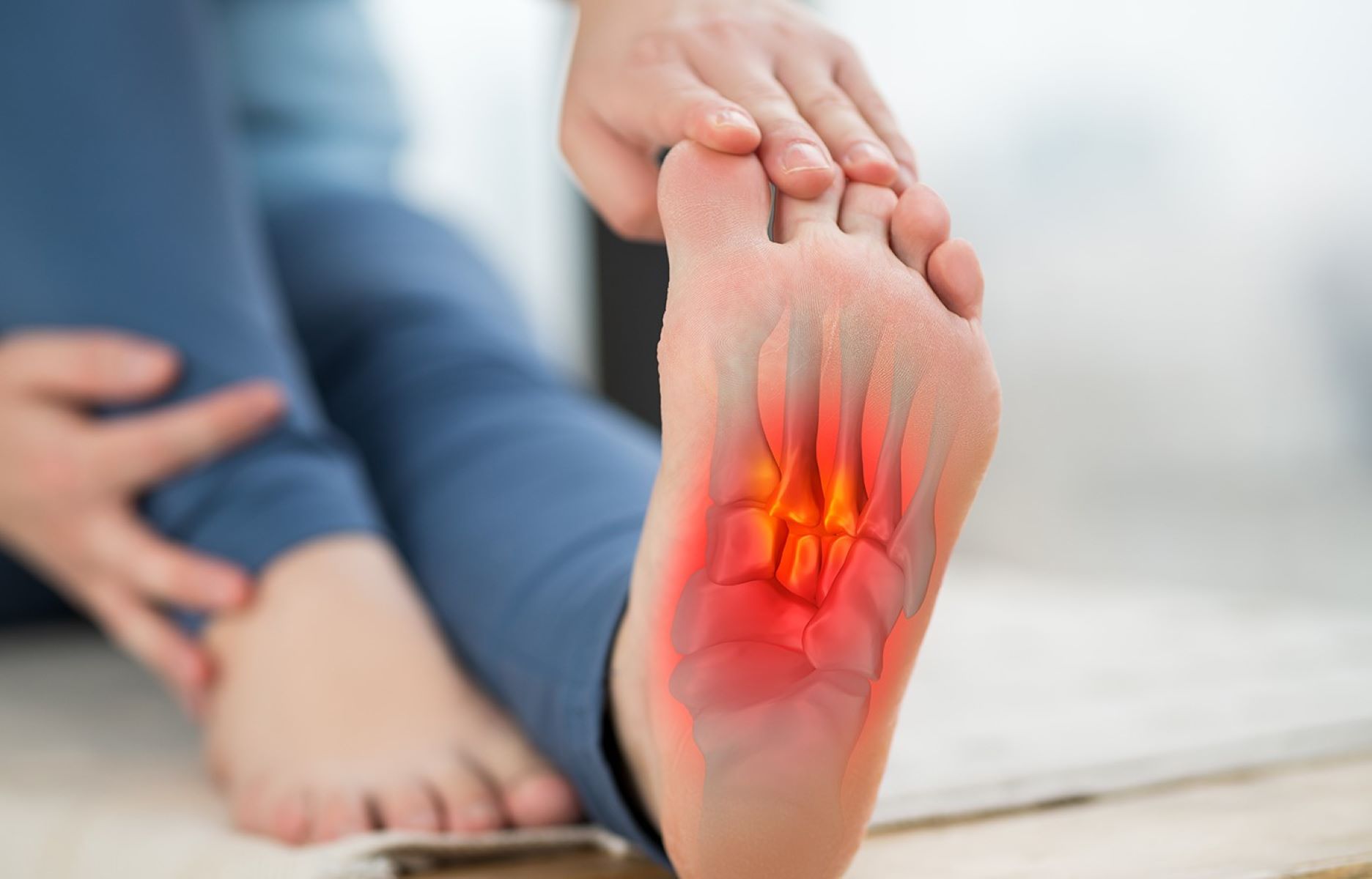
Understanding the link between excessive coffee consumption and arthritis
Arthritis, a common yet debilitating condition, encompasses a range of joint disorders that cause pain, stiffness, and swelling. While the precise causes of arthritis are multifaceted, research has unveiled a potential link between excessive coffee consumption and an increased risk of developing certain forms of arthritis.
The association between coffee intake and arthritis risk has been a subject of scientific inquiry, with studies suggesting that excessive coffee consumption may exacerbate the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. This correlation is attributed to the presence of certain compounds in coffee, including caffeine and polyphenols, which can trigger inflammatory responses in the body.
Caffeine, a central nervous system stimulant found abundantly in coffee, has been implicated in promoting inflammation, which is a key factor in the progression of arthritis. Furthermore, excessive caffeine intake has been linked to heightened levels of homocysteine, an amino acid associated with inflammation and joint damage, thereby potentially exacerbating arthritis symptoms.
Moreover, the polyphenols present in coffee, while known for their antioxidant properties, may also contribute to the inflammatory processes underlying arthritis. These compounds have been shown to interact with the body's immune system, potentially leading to an overactive immune response that exacerbates joint inflammation and tissue damage.
It is important to note that individual responses to coffee consumption can vary, and not everyone who drinks coffee excessively will develop arthritis. However, for individuals already predisposed to arthritis or experiencing its symptoms, excessive coffee intake may exacerbate the condition, leading to increased discomfort and reduced joint mobility.
In light of these findings, individuals with a family history of arthritis or those already diagnosed with the condition may benefit from moderating their coffee consumption. By reducing excessive coffee intake, they may potentially alleviate the inflammatory burden on their joints and mitigate the progression of arthritis symptoms.
As we continue to unravel the intricate relationship between excessive coffee consumption and arthritis, it becomes evident that mindful dietary choices play a pivotal role in managing arthritis risk. By staying informed and making conscious decisions about our coffee consumption, we can take proactive steps toward safeguarding our joint health and overall well-being.
The potential impact of excessive coffee consumption on obesity risk
Excessive coffee consumption has been a subject of growing interest in relation to its potential impact on obesity risk. While coffee is often celebrated for its metabolism-boosting properties and ability to enhance fat burning, the effects of excessive coffee intake on weight management and obesity risk are multifaceted.
One of the primary concerns regarding the link between excessive coffee consumption and obesity risk lies in the realm of added calories from high-calorie coffee beverages. Popular coffee concoctions such as flavored lattes, mochas, and frappuccinos often contain significant amounts of sugar, syrups, and whipped cream, contributing to a substantial calorie load. Consuming these calorie-dense coffee drinks regularly can lead to an increased overall calorie intake, potentially tipping the balance toward weight gain and obesity.
Furthermore, the potential impact of caffeine, a prominent component of coffee, on appetite and food cravings warrants consideration in the context of obesity risk. While caffeine has been shown to temporarily suppress appetite and increase energy expenditure, excessive caffeine consumption may disrupt appetite regulation and lead to erratic eating patterns. This can potentially result in overeating and a higher consumption of calorie-dense foods, contributing to weight gain and an elevated risk of obesity.
Moreover, the intricate interplay between coffee consumption, cortisol levels, and stress responses may influence obesity risk. Excessive caffeine intake can stimulate the release of cortisol, a hormone associated with stress and the regulation of metabolism. Elevated cortisol levels, particularly in response to chronic stress, have been linked to increased abdominal fat deposition and a higher susceptibility to obesity. Therefore, individuals who consume excessive amounts of coffee, especially in conjunction with high stress levels, may be at an augmented risk of developing obesity.
It is important to note that individual responses to coffee consumption and its potential impact on obesity risk can vary. While some individuals may experience minimal effects on their weight and metabolism from moderate coffee intake, others, particularly those predisposed to obesity, may be more susceptible to the adverse consequences of excessive coffee consumption.
In light of these considerations, individuals concerned about obesity risk should approach their coffee consumption with mindfulness and moderation. Opting for simpler, lower-calorie coffee options and being mindful of added sugars and syrups can help mitigate the calorie burden associated with coffee beverages. Additionally, being attuned to one's caffeine tolerance and its potential effects on appetite and stress responses can aid in managing the impact of coffee consumption on obesity risk.
As we navigate the complex landscape of coffee consumption and its potential implications for obesity risk, it becomes evident that informed choices and moderation are key in promoting a balanced approach to coffee intake. By staying mindful of the potential impact of excessive coffee consumption on obesity risk, individuals can strive for a harmonious relationship with this beloved beverage while prioritizing their overall health and well-being.
Managing coffee intake for individuals at risk of arthritis and obesity
For individuals at risk of arthritis and obesity, managing coffee intake is a crucial aspect of maintaining their overall health and well-being. By adopting mindful strategies and making informed choices, these individuals can navigate their relationship with coffee to mitigate potential risks and promote a balanced lifestyle.
Moderation is Key
Moderating coffee intake is paramount for individuals at risk of arthritis and obesity. While moderate coffee consumption has been associated with certain health benefits, excessive intake may exacerbate the symptoms of arthritis and contribute to obesity risk. Therefore, setting limits on daily coffee consumption can help mitigate these potential adverse effects. By being mindful of portion sizes and frequency of coffee consumption, individuals can strike a balance that aligns with their health goals.
Opting for Healthier Alternatives
Choosing healthier coffee alternatives can be beneficial for individuals at risk of arthritis and obesity. Instead of indulging in calorie-laden coffee beverages laden with sugars and syrups, opting for simpler options such as black coffee or adding minimal amounts of natural sweeteners can help reduce the calorie burden associated with coffee consumption. Additionally, incorporating non-dairy milk alternatives and avoiding excessive creamers can contribute to a healthier coffee-drinking experience.
Being Mindful of Caffeine Intake
Being mindful of caffeine intake is essential for individuals at risk of arthritis and obesity. While caffeine can provide a temporary energy boost, excessive consumption may exacerbate inflammation associated with arthritis and disrupt appetite regulation, potentially contributing to obesity risk. Therefore, individuals should be attuned to their caffeine tolerance and consider opting for decaffeinated coffee or reducing overall caffeine intake to manage potential adverse effects.
Considering Individual Sensitivities
Considering individual sensitivities to coffee is crucial for those at risk of arthritis and obesity. Not everyone responds to coffee consumption in the same way, and some individuals may be more susceptible to the potential negative effects of excessive coffee intake. By paying attention to their body's responses and consulting with healthcare professionals, individuals can tailor their coffee consumption to align with their unique sensitivities and mitigate potential risks.
Embracing a Holistic Approach
Embracing a holistic approach to managing coffee intake involves considering the broader dietary and lifestyle factors that intersect with coffee consumption. Individuals at risk of arthritis and obesity can benefit from incorporating a balanced and varied diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress levels. By integrating these elements into their overall wellness strategy, individuals can cultivate a harmonious relationship with coffee while prioritizing their health and mitigating potential risks.
In essence, managing coffee intake for individuals at risk of arthritis and obesity entails embracing moderation, choosing healthier alternatives, being mindful of caffeine intake, considering individual sensitivities, and adopting a holistic approach to wellness. By integrating these strategies into their daily routine, individuals can navigate their coffee consumption in a manner that supports their overall health and well-being.
Conclusion and recommendations
In summary, the potential negative effects of excessive coffee consumption on arthritis and obesity risk underscore the importance of mindful and informed dietary choices. While coffee remains a beloved beverage enjoyed by millions, its impact on health, particularly concerning arthritis and obesity, warrants careful consideration. As individuals navigate their relationship with coffee, it is essential to prioritize moderation, mindful consumption, and a holistic approach to wellness.
Recommendations for managing coffee intake in light of arthritis and obesity risk include:
-
Moderation: Setting limits on daily coffee consumption to mitigate potential adverse effects on arthritis and obesity risk.
-
Healthier Alternatives: Opting for simpler, lower-calorie coffee options and minimizing the use of added sugars and syrups to reduce the calorie burden associated with coffee beverages.
-
Caffeine Awareness: Being mindful of caffeine intake and considering decaffeinated coffee or reduced caffeine options to manage potential adverse effects on inflammation and appetite regulation.
-
Individual Sensitivities: Paying attention to individual responses to coffee consumption and tailoring intake based on unique sensitivities and health considerations.
-
Holistic Wellness: Embracing a holistic approach to wellness by integrating balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and stress management into daily routines.
By incorporating these recommendations into their lifestyle, individuals can cultivate a balanced and mindful approach to coffee consumption, thereby supporting their overall health and well-being. It is important to remember that the impact of coffee consumption can vary among individuals, and consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance based on individual health profiles and considerations.
As we move forward, it is crucial to approach coffee consumption with awareness and mindfulness, recognizing that informed choices can empower individuals to enjoy this beloved beverage while safeguarding their health. By staying attuned to the potential implications of excessive coffee consumption on arthritis and obesity risk, individuals can make conscious decisions that align with their wellness goals, ultimately fostering a harmonious and balanced lifestyle.
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between excessive coffee consumption and arthritis and obesity risk underscores the significance of informed choices and moderation. By integrating these principles into their daily lives, individuals can navigate their coffee consumption in a manner that supports their overall health and well-being.