Home>Training & Techniques>3 Exercises To Improve Hamstring Flexibility


Training & Techniques
3 Exercises To Improve Hamstring Flexibility
Published: February 28, 2024
Improve your hamstring flexibility with these 3 effective exercises. Discover training and techniques to enhance your flexibility and prevent injury.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
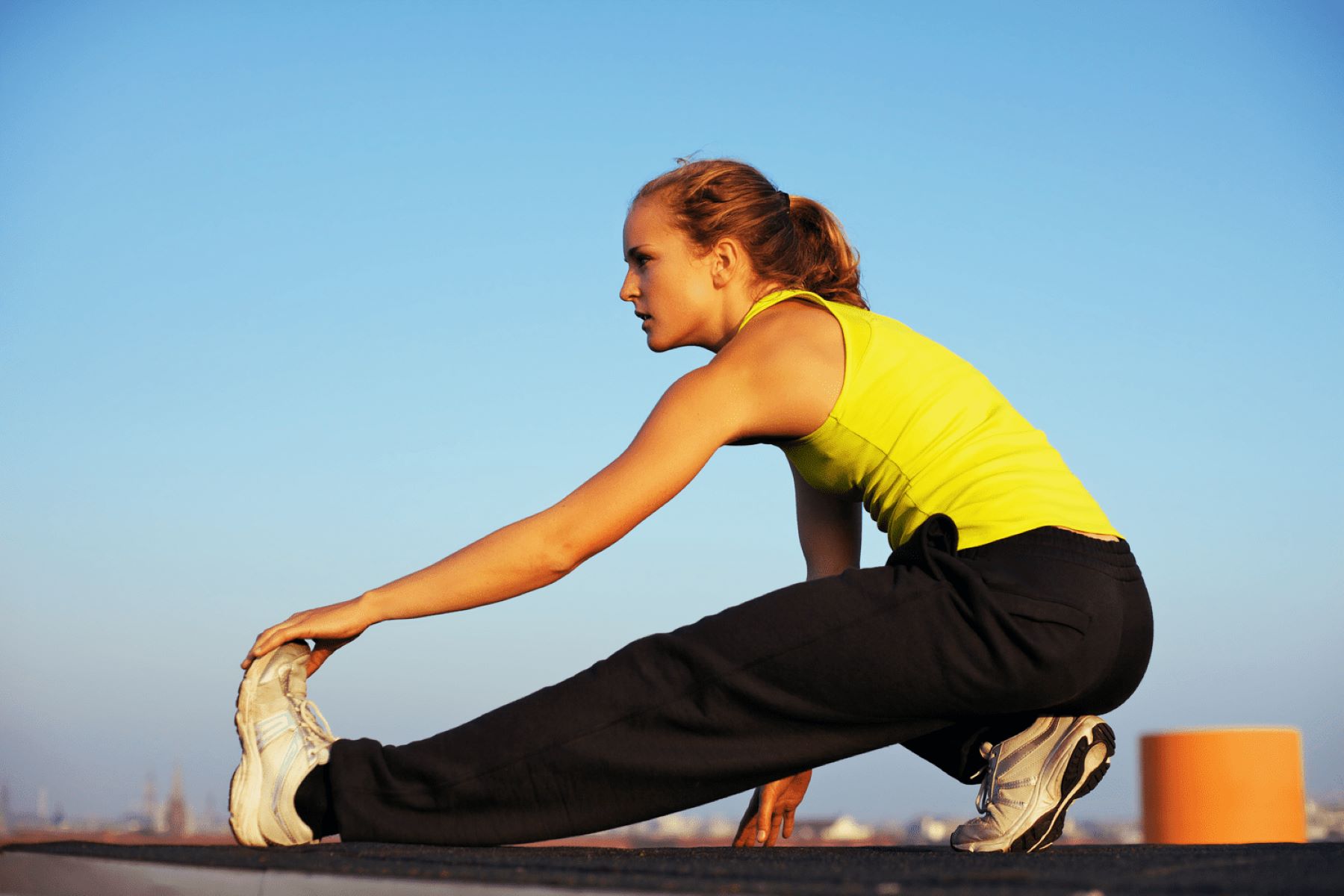
Importance of Hamstring Flexibility
Hamstring flexibility plays a crucial role in our overall well-being and physical performance. The hamstrings, a group of three muscles located at the back of the thigh, are essential for various daily activities and athletic endeavors. Here's why maintaining optimal hamstring flexibility is so important:
-
Enhanced Range of Motion: Flexible hamstrings allow for improved range of motion in the hips and lower back. This not only aids in performing daily activities such as bending, walking, and sitting but also contributes to better athletic performance in activities like running, jumping, and kicking.
-
Injury Prevention: Tight hamstrings can increase the risk of injuries, particularly in the lower back and knees. By maintaining flexibility in these muscles, individuals can reduce the likelihood of strains, tears, and other related injuries. This is especially beneficial for athletes and individuals who engage in physical activities regularly.
-
Posture and Back Health: Tight hamstrings can contribute to poor posture and lower back pain. By keeping the hamstrings flexible, individuals can alleviate tension in the lower back and improve their overall posture, leading to reduced discomfort and a decreased risk of chronic back issues.
-
Functional Movement: Flexible hamstrings are essential for maintaining functional movement patterns. Whether it's bending down to pick something up, reaching for an object, or performing dynamic movements in sports, having flexible hamstrings allows for smoother and more efficient movement patterns.
-
Balance and Stability: Optimal hamstring flexibility contributes to better balance and stability. This is particularly important for older adults, as it can help reduce the risk of falls and related injuries.
Incorporating hamstring flexibility exercises into your regular fitness routine can yield numerous benefits, from improved physical performance to reduced risk of injury and enhanced overall well-being. By prioritizing the flexibility of these crucial muscles, individuals can experience a positive impact on their daily activities and athletic pursuits.
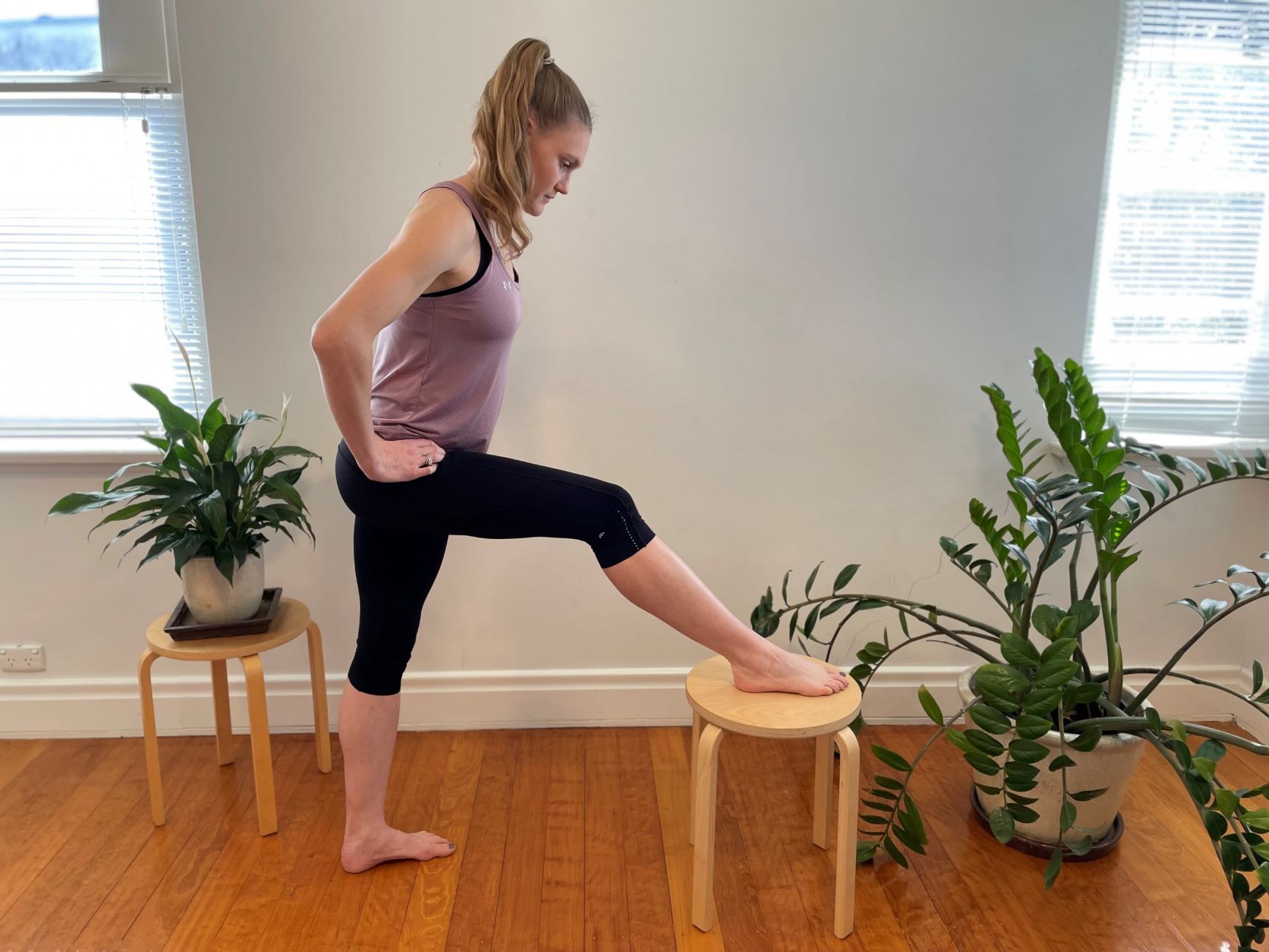
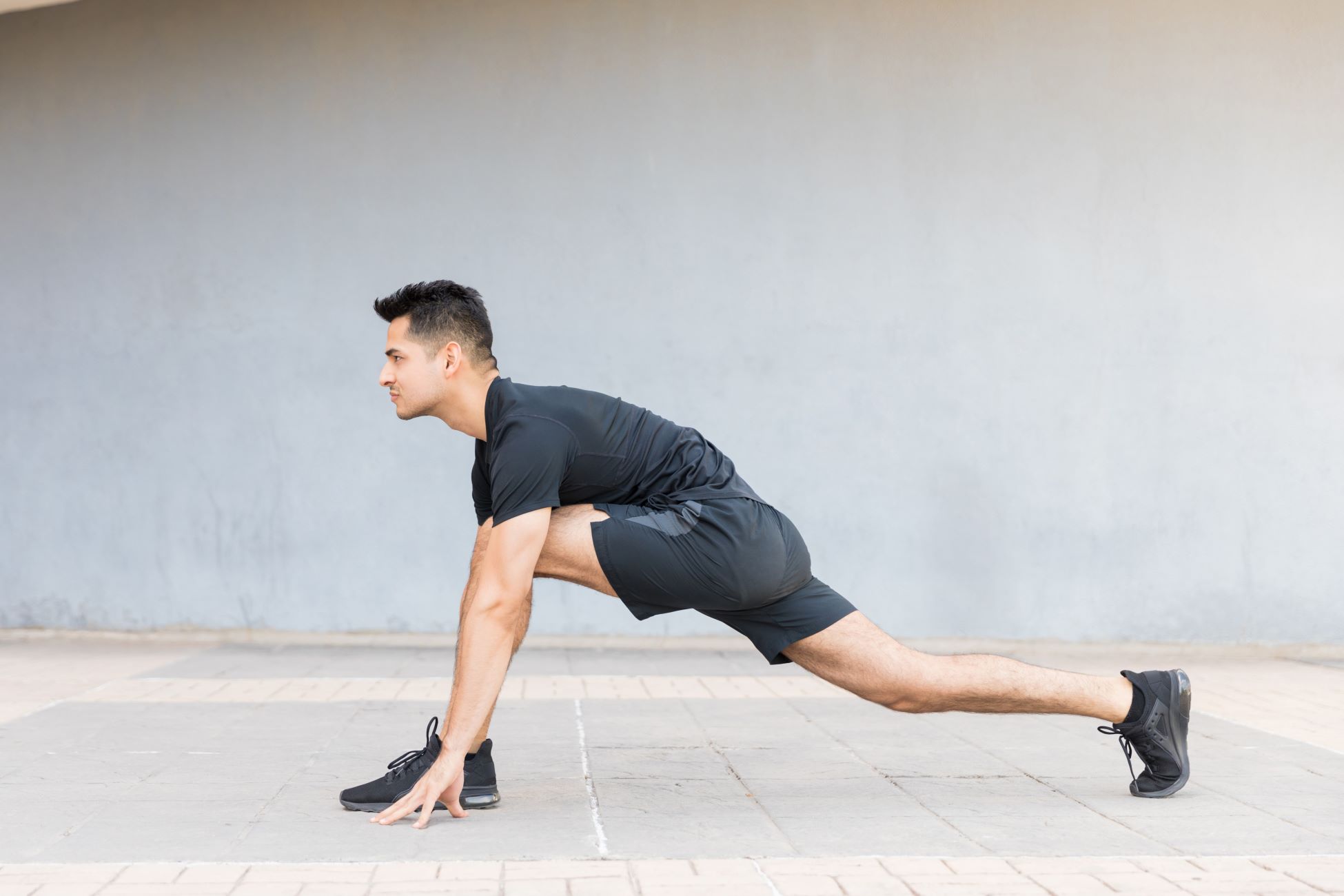
Exercise 1: Standing Hamstring Stretch
The standing hamstring stretch is a simple yet effective exercise that targets the hamstring muscles, promoting flexibility and mobility in the lower body. This exercise can be performed virtually anywhere, making it a convenient addition to any fitness routine. To execute the standing hamstring stretch:
-
Starting Position: Begin by standing upright with your feet hip-width apart. Ensure that your posture is tall and your shoulders are relaxed.
-
Execution: Extend one leg forward with a slight bend in the knee and keep the other leg straight. Slowly hinge at the hips, leaning your torso forward while keeping your back straight. Reach toward your extended foot, aiming to feel a gentle stretch in the back of the thigh of the extended leg. Hold this position for 15-30 seconds while breathing deeply and then return to the starting position. Repeat the stretch on the other leg.
-
Key Points: It's important to avoid rounding your back during the stretch, as this can diminish the effectiveness of the exercise. Instead, focus on maintaining a straight back and feeling the stretch in the targeted hamstring muscles.
The standing hamstring stretch offers several benefits, including:
-
Improved Flexibility: By regularly performing this stretch, individuals can gradually increase the flexibility of their hamstring muscles, leading to improved range of motion in the hips and lower back.
-
Injury Prevention: Flexible hamstrings are less prone to strains and tears, reducing the risk of injury during physical activities and sports.
-
Post-Workout Recovery: Incorporating this stretch into a post-workout routine can aid in reducing muscle tension and promoting recovery after exercise.
-
Enhanced Functional Movement: Flexible hamstrings contribute to better functional movement patterns, allowing individuals to perform daily activities with greater ease and efficiency.
-
Relief from Lower Back Discomfort: Stretching the hamstrings can alleviate tension in the lower back, potentially reducing discomfort and promoting better posture.
Incorporating the standing hamstring stretch into a regular exercise regimen can contribute to overall lower body flexibility and function. It is important to perform this stretch gently and gradually increase the intensity over time to avoid overstretching the muscles. By prioritizing the flexibility of the hamstrings through exercises like the standing hamstring stretch, individuals can experience improved physical performance and a reduced risk of muscle-related injuries.
Exercise 2: Seated Forward Fold
The seated forward fold, also known as Paschimottanasana in yoga, is a highly effective exercise for enhancing hamstring flexibility and promoting overall lower body mobility. This seated posture provides a deep stretch to the entire back of the body, targeting the hamstrings, lower back, and calves. Incorporating the seated forward fold into a regular fitness routine can yield numerous benefits, contributing to improved flexibility, reduced muscle tension, and enhanced functional movement patterns.
To perform the seated forward fold:
-
Starting Position: Begin by sitting on the floor with your legs extended in front of you. Ensure that your spine is tall and your shoulders are relaxed. Flex your feet, pointing your toes toward the ceiling.
-
Execution: Inhale deeply, lengthening your spine, and as you exhale, hinge at the hips and lean forward. Reach for your feet or shins, aiming to bring your chest closer to your thighs. It's important to maintain a straight spine throughout the movement, avoiding rounding the back. Hold the forward fold for 30-60 seconds while breathing deeply and feeling the stretch along the back of your legs.
-
Modifications: For individuals with limited flexibility, it's acceptable to bend the knees slightly to reduce the intensity of the stretch. Over time, as flexibility improves, gradually work toward straightening the legs in the forward fold.
The seated forward fold offers a multitude of benefits, including:
-
Improved Hamstring Flexibility: This exercise provides a deep stretch to the hamstrings, gradually increasing their flexibility and range of motion.
-
Reduced Muscle Tension: Regular practice of the seated forward fold can help alleviate tension in the lower back and hamstrings, promoting relaxation and reducing discomfort.
-
Enhanced Posture: Stretching the back of the body in this manner can contribute to improved posture by releasing tightness in the lower back and promoting spinal alignment.
-
Stress Relief: The gentle compression of the abdomen in the forward fold can have a calming effect on the nervous system, aiding in stress reduction and relaxation.
-
Improved Circulation: The seated forward fold can stimulate blood flow to the pelvic region and lower back, promoting better circulation and potentially alleviating discomfort associated with prolonged sitting.
Incorporating the seated forward fold into a regular exercise routine, whether as part of a yoga practice or a standalone stretch, can contribute to overall lower body flexibility and well-being. It's important to approach this exercise with patience and mindfulness, gradually deepening the stretch over time to avoid overexertion. By prioritizing the flexibility of the hamstrings through exercises like the seated forward fold, individuals can experience improved physical performance and a reduced risk of muscle-related injuries.
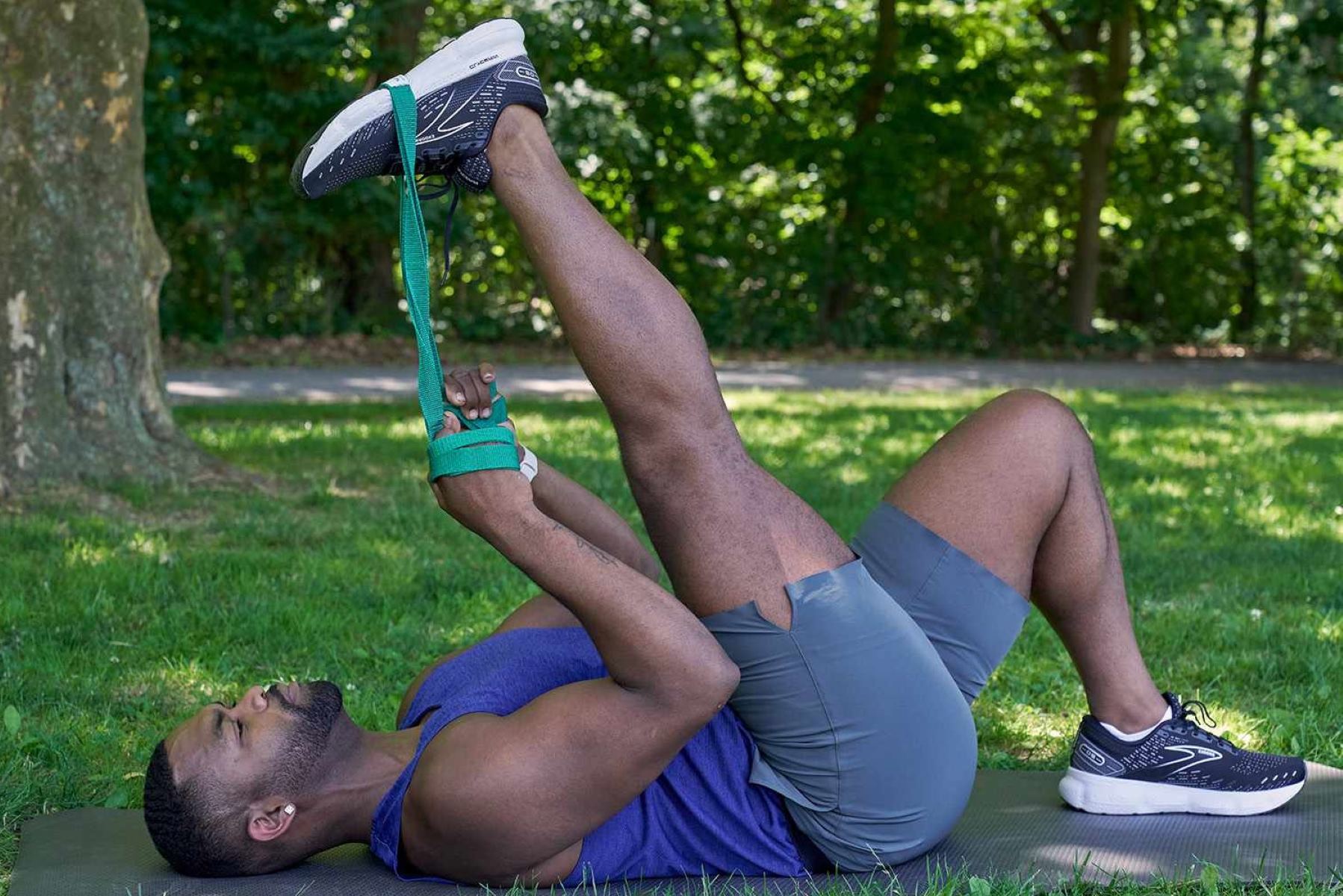
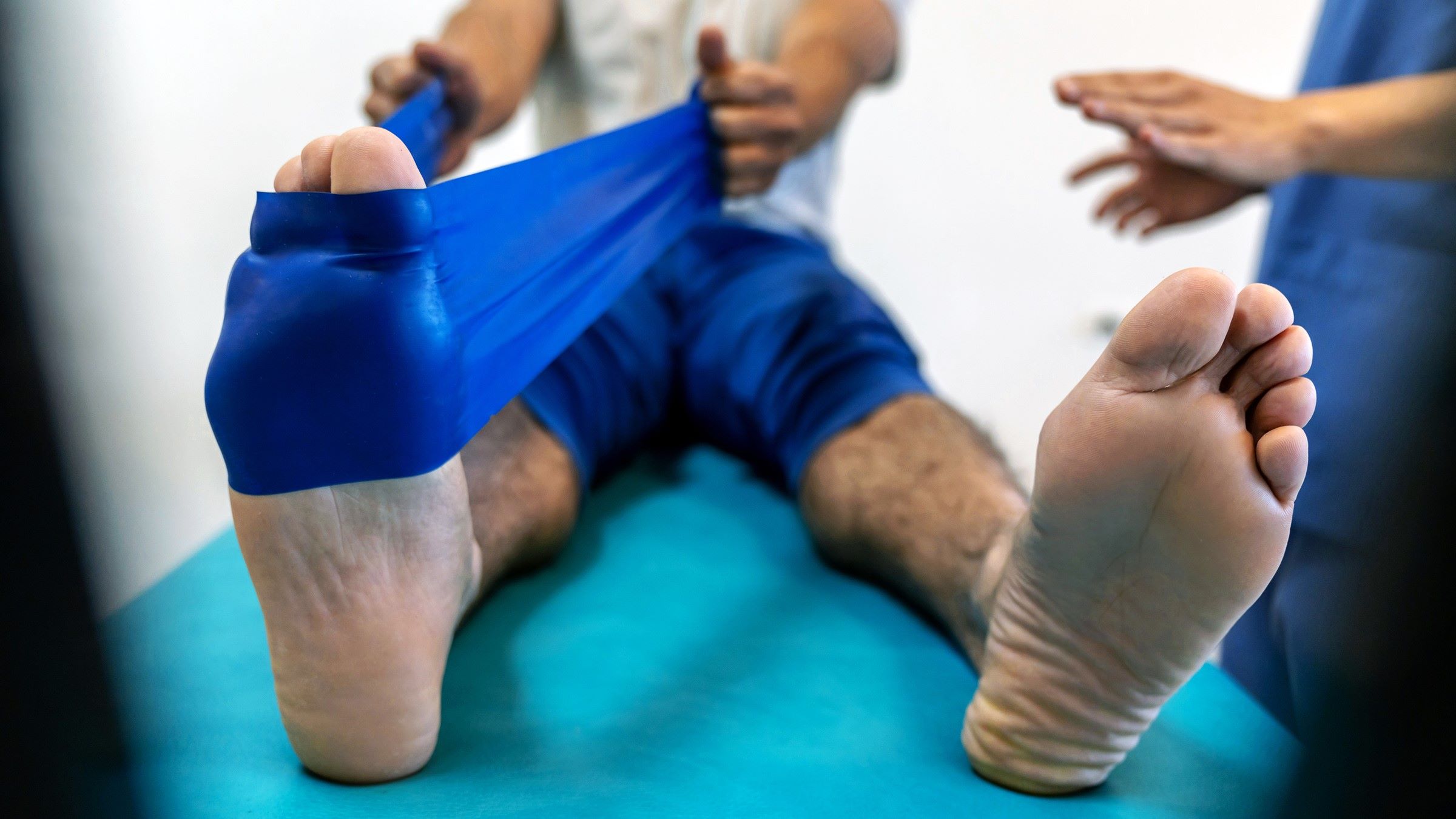
Exercise 3: Supine Hamstring Stretch
The supine hamstring stretch, also known as the lying hamstring stretch, is a highly effective exercise for targeting and enhancing the flexibility of the hamstring muscles. This exercise is particularly beneficial for individuals of all fitness levels, as it can be performed with ease and requires minimal space. The supine hamstring stretch provides a deep and controlled stretch to the hamstrings, promoting increased flexibility and mobility in the lower body.
To perform the supine hamstring stretch:
-
Starting Position: Begin by lying on your back with both legs extended along the floor. Ensure that your spine is in a neutral position, and your arms are relaxed by your sides.
-
Execution: Lift one leg off the floor, keeping the knee slightly bent. Using both hands, clasp behind the thigh of the lifted leg, gently pulling it toward your chest. As you do so, aim to straighten the knee while feeling a comfortable stretch in the back of the thigh. Hold this position for 30-60 seconds, breathing deeply and allowing the muscles to relax. Repeat the stretch with the opposite leg.
-
Modifications: For individuals with limited flexibility, a yoga strap or towel can be used to loop around the foot of the lifted leg, providing support and assistance in achieving the stretch. This modification allows individuals to gradually increase the intensity of the stretch as flexibility improves over time.
The supine hamstring stretch offers a range of benefits, including:
-
Increased Flexibility: This exercise targets the hamstrings, gradually enhancing their flexibility and range of motion, which is essential for various daily activities and physical performance.
-
Improved Muscle Recovery: Incorporating the supine hamstring stretch into a post-workout routine can aid in reducing muscle tension and promoting recovery after exercise, contributing to overall muscle health.
-
Enhanced Lower Body Mobility: By regularly performing this stretch, individuals can experience improved mobility in the lower body, particularly in the hamstrings and surrounding muscles, leading to better functional movement patterns.
-
Alleviation of Lower Back Discomfort: The controlled stretch provided by the supine hamstring stretch can help alleviate tension in the lower back, potentially reducing discomfort and promoting better posture.
-
Injury Prevention: Flexible hamstrings are less prone to strains and tears, reducing the risk of injury during physical activities and sports, making this exercise an important component of injury prevention.
Incorporating the supine hamstring stretch into a regular exercise routine can contribute to overall lower body flexibility and function. It is important to approach this exercise with mindfulness, focusing on controlled movements and gradual progression to avoid overexertion. By prioritizing the flexibility of the hamstrings through exercises like the supine hamstring stretch, individuals can experience improved physical performance and a reduced risk of muscle-related injuries.