Home>Health & Nutrition>The Essentials Of Fungal Toenail Infections

Health & Nutrition
The Essentials Of Fungal Toenail Infections
Published: February 24, 2024
Learn about the essentials of fungal toenail infections and how they can impact your health and nutrition. Find expert advice and tips for prevention and treatment.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Therunningadvisor.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Fungal Toenail Infections
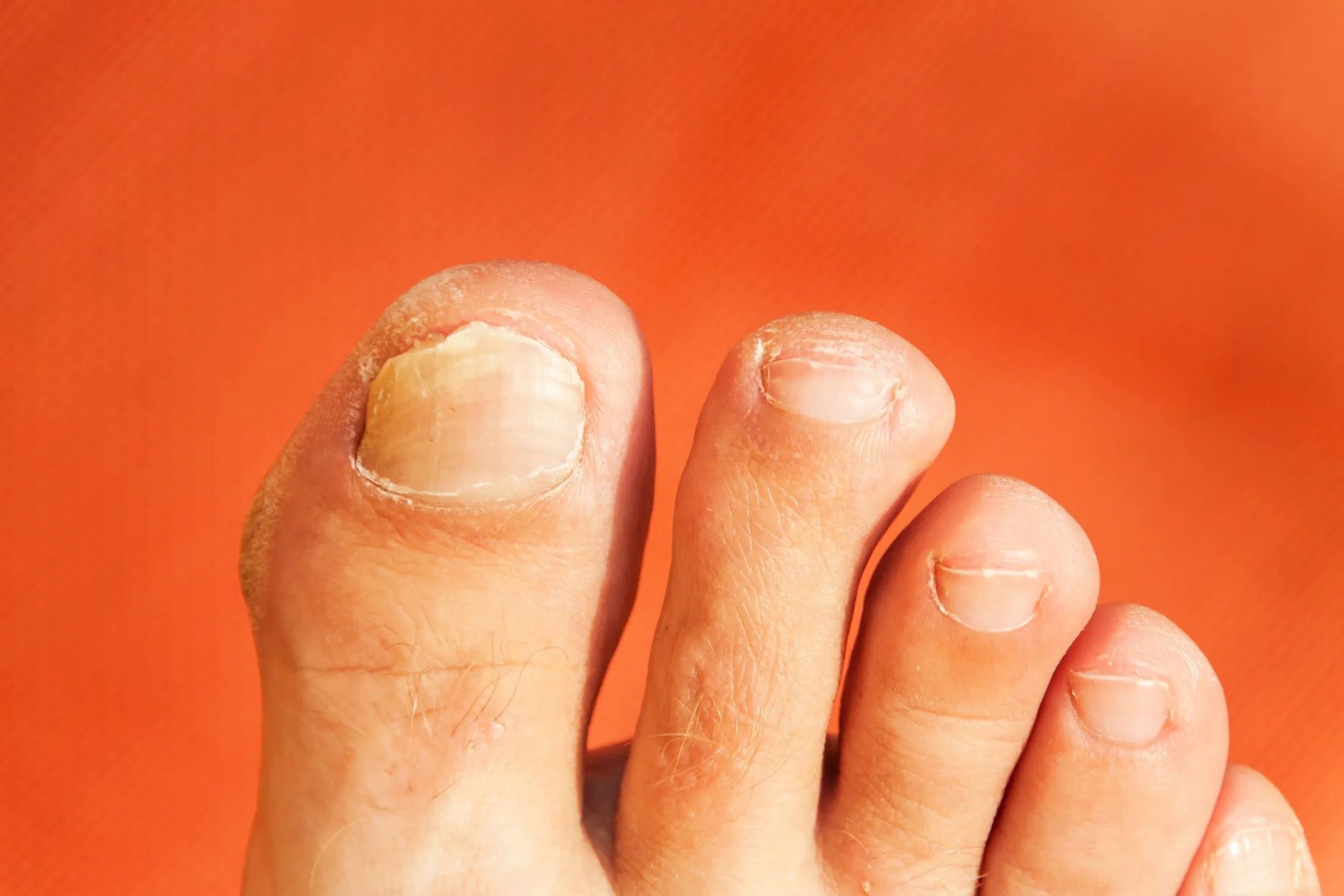
Fungal toenail infections, also known as onychomycosis, are common conditions that occur when a fungus infects the toenails. This type of infection typically begins as a white or yellow spot under the tip of the toenail and can cause the nail to thicken, discolor, and crumble at the edge. Fungal toenail infections are often challenging to treat and can cause discomfort or pain, impacting an individual's quality of life.
The most common culprit behind fungal toenail infections is a group of fungi called dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making the feet an ideal breeding ground. Additionally, yeast and molds can also cause toenail infections. These fungi can enter the skin through tiny cuts or separations between the nail and the nail bed, leading to an infection.
Fungal toenail infections are more prevalent in older adults due to reduced blood circulation, more years of exposure to fungi, and slower nail growth. Furthermore, individuals with a weakened immune system, diabetes, or a history of athlete's foot are at a higher risk of developing fungal toenail infections. Moreover, factors such as wearing closed-toe shoes for extended periods, walking barefoot in damp communal areas like swimming pools or gyms, and having a family history of fungal infections can also increase the likelihood of developing this condition.
Understanding the nature of fungal toenail infections is crucial for effective management and prevention. By recognizing the causes and risk factors associated with this condition, individuals can take proactive measures to minimize the risk of infection and seek appropriate treatment if needed.
Read more: Prevent Toenail Issues While Running
Causes and Risk Factors
Fungal toenail infections, also known as onychomycosis, are primarily caused by various types of fungi, with dermatophytes being the most common culprits. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making the feet an ideal breeding ground. When the toenails are continuously exposed to such conditions, the risk of developing a fungal infection significantly increases. Additionally, yeast and molds can also lead to toenail infections, contributing to the diverse range of pathogens responsible for this condition.
Several risk factors can predispose individuals to fungal toenail infections. Older adults are particularly susceptible due to reduced blood circulation, more years of exposure to fungi, and slower nail growth. These factors create an environment where fungi can thrive and cause infections. Furthermore, individuals with a weakened immune system, such as those with diabetes or HIV, are at a higher risk of developing fungal toenail infections. The compromised immune response makes it more challenging for the body to combat fungal invasions, leading to an increased susceptibility to infections.
Moreover, individuals with a history of athlete's foot, a common fungal infection that affects the skin of the feet, are more prone to developing fungal toenail infections. The fungus responsible for athlete's foot can spread to the toenails, leading to a more severe and persistent infection. Additionally, genetic predisposition plays a role, as individuals with a family history of fungal infections may have a higher likelihood of developing toenail fungus.
Lifestyle and environmental factors also contribute to the risk of fungal toenail infections. Wearing closed-toe shoes for extended periods creates a conducive environment for fungal growth, especially if the feet perspire excessively. Walking barefoot in damp communal areas like swimming pools, gyms, and public showers increases the risk of coming into contact with fungi, potentially leading to an infection. Furthermore, individuals who frequently experience minor nail injuries or have nail deformities are more susceptible to fungal toenail infections, as these conditions create entry points for fungi to invade the nails.
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with fungal toenail infections is essential for proactive prevention and effective management. By recognizing these factors, individuals can take preventive measures to minimize the risk of infection and seek appropriate treatment if needed.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Fungal toenail infections can manifest through various symptoms, indicating the presence of an underlying fungal invasion. Initially, the infected toenail may appear as a small white or yellow spot under the tip. As the infection progresses, the nail may thicken, become brittle, and develop a distorted shape. In some cases, the affected nail may crumble at the edges or separate from the nail bed. Additionally, the infected toenail may exhibit discoloration, turning yellow, brown, or even black. Furthermore, individuals with fungal toenail infections may experience discomfort or pain in the affected toe, especially when wearing shoes or walking.
Diagnosing a fungal toenail infection typically involves a comprehensive assessment of the affected toenail and, in some cases, laboratory testing. Healthcare providers may visually inspect the toenail to identify common signs of a fungal infection, such as discoloration, thickening, or crumbling. In certain instances, a sample of the affected nail may be collected for further analysis. This sample is examined under a microscope or sent to a laboratory for fungal culture, allowing for the identification of the specific fungus responsible for the infection.
In addition to visual inspection and laboratory testing, healthcare providers may inquire about the individual's medical history and any previous instances of fungal infections. Understanding the patient's history can provide valuable insights into potential risk factors and predisposing conditions that may contribute to the development of a fungal toenail infection. Furthermore, discussing symptoms and any discomfort experienced by the individual can aid in the accurate diagnosis of the condition.
It is important to note that fungal toenail infections share similarities with other nail conditions, such as psoriasis or bacterial infections. Therefore, a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis. By recognizing the distinct symptoms associated with fungal toenail infections and employing appropriate diagnostic methods, healthcare providers can effectively identify and confirm the presence of a fungal invasion in the toenail.
Early diagnosis of fungal toenail infections is essential for initiating timely treatment and preventing the spread of the infection to other nails or individuals. By promptly addressing the condition, individuals can minimize the impact of the infection and work towards restoring the health and appearance of their toenails.
Treatment Options
Addressing fungal toenail infections involves a multifaceted approach aimed at eradicating the underlying fungal invasion and promoting the restoration of healthy toenails. Treatment options for fungal toenail infections encompass various strategies, ranging from topical antifungal medications to oral therapies and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
Topical Antifungal Medications
Topical antifungal medications, available in the form of creams, ointments, or nail lacquers, are commonly utilized as a first-line treatment for mild to moderate fungal toenail infections. These medications are applied directly to the affected toenail and surrounding skin, allowing the antifungal agents to penetrate the nail and combat the underlying fungal growth. Regular application as prescribed by a healthcare provider is essential to achieve optimal results. While topical treatments are effective for some individuals, they may require prolonged use and consistent adherence to the treatment regimen.
Oral Antifungal Therapies
In cases of more severe or persistent fungal toenail infections, oral antifungal medications may be recommended. These systemic treatments are ingested and work from within the body to target the fungal infection. Oral antifungal therapies are often more potent than topical medications and can effectively combat stubborn fungal invasions. However, they may be associated with a higher risk of side effects and require close monitoring by a healthcare provider. Additionally, oral antifungal therapies typically necessitate a longer treatment duration to ensure the complete eradication of the fungal infection.
Combination Therapy
In certain instances, healthcare providers may prescribe a combination of topical and oral antifungal treatments to address fungal toenail infections comprehensively. This approach aims to maximize the efficacy of the treatment by targeting the infection through both topical application and systemic action. By combining different treatment modalities, healthcare providers can tailor the approach to the individual's specific condition, considering factors such as the extent of the infection, overall health, and potential contraindications.
Surgical Interventions
For severe cases of fungal toenail infections that do not respond to conventional treatments, surgical interventions may be considered. Procedures such as partial or complete nail removal, laser therapy, or debridement can be employed to eliminate the infected nail and promote the growth of a healthy nail. Surgical interventions are typically reserved for persistent infections or cases where the toenail is significantly damaged. These procedures are performed under the guidance of a healthcare professional and aim to address the infection while minimizing the impact on the overall nail structure.
Adjunctive Measures
In addition to specific antifungal treatments, adjunctive measures play a crucial role in managing fungal toenail infections. Proper foot hygiene, including regular washing and thorough drying of the feet, can help prevent the spread of the infection and create an environment less conducive to fungal growth. Furthermore, wearing breathable footwear and changing socks frequently can aid in maintaining foot hygiene and reducing the risk of recurrent infections.
Consultation with a Healthcare Provider
It is essential for individuals with fungal toenail infections to seek guidance from a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on the severity of the infection, overall health, and individual preferences. Healthcare providers can offer personalized recommendations and monitor the progress of the treatment to ensure optimal outcomes.
By exploring the diverse treatment options available for fungal toenail infections and considering individualized approaches, individuals can take proactive steps towards addressing the condition and restoring the health and appearance of their toenails.
Prevention and Management
Preventing and effectively managing fungal toenail infections is essential for maintaining optimal foot health and minimizing the risk of recurrent infections. By implementing proactive measures and adopting healthy foot care practices, individuals can reduce their susceptibility to fungal toenail infections and promote overall nail wellness.
Foot Hygiene
Maintaining proper foot hygiene is a cornerstone of preventing fungal toenail infections. Regularly washing the feet with soap and water, particularly after being in communal areas or engaging in activities that lead to perspiration, can help remove fungi and prevent their proliferation. Thoroughly drying the feet, especially between the toes, is crucial, as fungi thrive in moist environments. Additionally, using a separate towel for the feet and ensuring it is completely dry can aid in preventing the spread of fungi.
Footwear Selection
Choosing appropriate footwear plays a significant role in preventing fungal toenail infections. Opting for breathable shoes made of natural materials, such as leather, can promote air circulation and reduce moisture accumulation, creating an environment less conducive to fungal growth. Additionally, wearing moisture-wicking socks and changing them regularly can help maintain foot hygiene and minimize the risk of fungal infections.
Read more: The Essential 7 Strength Moves For Runners
Nail Care
Practicing proper nail care is vital for preventing fungal toenail infections. Keeping the toenails trimmed, straight across, and at a moderate length can reduce the likelihood of nail trauma and create an environment less susceptible to fungal invasion. Avoiding the use of sharp or shared instruments for nail care and promptly addressing any nail injuries can further minimize the risk of fungal infections.
Foot Protection
Taking measures to protect the feet from potential fungal exposure is essential for preventing toenail infections. Wearing sandals or protective footwear in communal areas like swimming pools, gyms, and public showers can reduce direct contact with fungi. Additionally, refraining from walking barefoot in these environments can help minimize the risk of fungal transmission.
Seeking Prompt Treatment
In the event of suspected fungal toenail infections or any changes in the toenails, seeking prompt evaluation and treatment from a healthcare provider is crucial. Early intervention can prevent the progression of the infection and minimize its impact on the affected toenail. Healthcare providers can offer personalized recommendations and treatment options tailored to the individual's specific condition, promoting effective management of fungal toenail infections.
Regular Foot Examinations
Conducting regular self-examinations of the feet and toenails can aid in early detection of any changes or signs of fungal infections. Being attentive to the appearance and texture of the toenails and promptly addressing any abnormalities can facilitate timely intervention and prevent the spread of the infection to other nails.
Healthy Lifestyle Practices
Maintaining overall health and well-being can contribute to the prevention of fungal toenail infections. Eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing underlying health conditions can support immune function and reduce the susceptibility to fungal invasions. Additionally, avoiding prolonged exposure to damp environments and taking measures to minimize foot perspiration can help create an environment less favorable for fungal growth.
By incorporating these preventive measures and adopting proactive foot care practices, individuals can effectively manage fungal toenail infections and reduce the risk of recurrent infections. Additionally, seeking guidance from healthcare providers and adhering to personalized recommendations can further support the prevention and management of fungal toenail infections, promoting overall foot health and well-being.